SSM的思考 MyBatis 重学的思考?
SqlSessionUtil工具类 工具类是不可少的,而创建工具类的代码都是一样的,直接复制粘贴即可下面的是写的第一个测试类 ,工具类在下面
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 package com.zzmr.mybatis.test;import com.zzmr.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper;import com.zzmr.mybatis.pojo.User;import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;import org.junit.Test;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.InputStream;public class MyBatisTest { @Test public void testInsert () throws IOException { InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml" ); SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder (); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(is); SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true ); UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); int result = mapper.insertUser(); System.out.println("结果:" + result); sqlSession.close(); } }
嘿嘿嘿代码来咯
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 package com.zzmr.mybatis.utils;import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.InputStream;public class SqlSessionUtil { public static SqlSession getSqlSession () { SqlSession sqlSession = null ; try { InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml" ); SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder (); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(is); sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true ); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return sqlSession; } }
先是创建输入流,要把mybatis的核心配置文件引入InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream(“mybatis-config.xml”);
获取SqlSessionFactoryBuilder对象SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
获取SqlSessionFactory类SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(is);
开启会话SqlSessionsqlSession = sqlSessionFactroy = sqlSessionFactroy.openSession(true)
其他问题 至于MyBatis编写顺序:
还有就是要注意查询操作,有一个很重要的点:
1 2 3 4 5 6 <select id ="getUserById" resultType ="com.zzmr.mybatis.pojo.User" > select * from t_user where id = 1; </select >
简言之就是一般就用resultType
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 <typeAliases > <package name ="com.zzmr.mybatis.pojo" /> </typeAliases >
哦对,一个很重要的问题:
1 2 3 4 MyBatis 核心配置文件中的标签必须要按照指定的顺序配置 The content of element type "configuration" must match "(properties?,settings?,typeAliases?,typeHandlers?,objectFactory?, objectWrapperFactory?,reflectorFactory?,plugins?,environments?,databaseIdProvider?,mappers?)"
也就是说引入properties文件的配置要在typeAliases上面个,不然会报错
有时候就很奇怪,就比如上面的typeAlias,比如说设置了别名abc,但是你只是改的一个地方的,剩下另一个resultType里面还是写的User,那即使只测一个方法,另一个还是会报错,要都改成abc才行,不过啊,还是直接在里面加一个package标签,name一设置,一个包就全部有别名了,多方便
自己写了一遍Emp的,写是写出来了,现在就有一个问题,就是数据库中的字段名和java中的属性名忘了怎么设置对应的了,驼峰什么的,问题不大,后面继续看
还有个小细节就是,在打包后的映射文件和接口会在同一个目录下(当然前提是配置时mapper接口和映射文件所在的包必须一致才行,mapper接口的名字和映射文件的名字必须也是一致才行)
做模板啥的没啥说的,再说以后大概率用不到MyBatis的配置文件(可能还会用,但是里面的内容会少得可怜)
MyBatis获取参数 步骤就是:
在方法上写上参数,比如根据用户名查询用户信息
1 User getUserByUsername (String username) ;
在映射文件中,要以’${username}’或者#{}代替之前直接写的参数,${}本质上就是字符串的拼接,#{}就是占位符赋值,使用$时要注意手动加上双引号,使用#并不需要
1 2 3 4 5 <select id ="getUserByUsername" resultType ="User" > select * from t_user where username = '${username}' </select >
注意:若是单个字面量类型的参数,两个都可以,但还是建议用#{}
注意问题
如果要是自己写的map集合,那获取的时候必须以自己设置的键获取,如果是直接放进去的数值,并没有自己建集合,那获取参数时只能使用arg0,arg1,或者param1,param2的方式获取
以后还是用#{}比较多,但是某些特殊的情况,还是必须使用${}的
如果是实体类类型的参数,就比如说:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 @Test public void testInsertUser () { SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.getSqlSession(); UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap <>(); User user = new User (null , "zzmr1" , "123456" , 33 , "女" , "0123@163.com" ); mapper.insertUser(user); }
这种情况,那在映射文件中,就要写成这种形式,可以通过实体类类型的属性名来获取属性值,属性名可不是简单的成员变量,而是set/get方法名去掉set/get剩下的内容(其实根成员变量区别不大)
1 2 3 4 <insert id ="insertUser" > insert into t_user values (null,#{username},#{password},#{age},#{gender},#{email}) </insert >
还有注解的形式
1 2 3 4 5 User getUserByUserNameByParam (@Param("ffff") String username) ;
1 2 3 4 <select id ="getUserByUserNameByParam" resultType ="User" > select * from t_user where username = #{ffff} </select >
这里获取参数的时候就是直接使用的Param注解里面的值(value) value是什么(ffff) 在映射文件中就以什么(ffff)获取
各种查询相关 若sql语句查询的结果为多条时,一定不能以实体类类型作为方法的返回值,否则会出现TooManyResultsException异常,若结果只有一条,可以以实体类类型,也可以使用list集合作为方法的返回值
查询用户总数量
1 2 3 4 5 6 Integer getCount () ;
映射文件:重点就是类型别名,大差小不差 Integer可以写成int/INT/Integer/integer都行
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 <select id ="getCount" resultType ="int" > select count(*) from t_user; </select >
测试类:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @Test public void testGetCount () { SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.getSqlSession(); SelectMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(SelectMapper.class); Integer count = mapper.getCount(); System.out.println(count); }
查询结果为map
这个List<Map<String,Object>>就很妙
1 2 3 4 List<Map<String,Object>> getAllUserToMap () ;
1 2 3 4 <select id ="getAllUserToMap" resultType ="map" > select * from t_user </select >
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @Test public void testGetAllUserToMap () { SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.getSqlSession(); SelectMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(SelectMapper.class); List<Map<String, Object>> alluser = mapper.getAllUserToMap(); for (Map<String, Object> map : alluser) { System.out.println(map); } }
特殊查询 模糊查询 虽然以后大部分情况都是使用#{}来实现,但是像模糊查询,还是可以使用${}的,但是用的也不多
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 <select id ="getUserByLikeByMe" resultType ="User" > select * from t_user where username like "%"#{mohu}"%" </select >
所以以后还是用这个比较多
1 select * from t_user where username like "%"#{mohu}"%"
批量删除 这种情况就是要用${}了
1 2 3 4 <delete id ="deleteByMe" > delete from t_user where id in (${ids}) </delete >
如果用#{},因为是在()里,而()里是不能加单引号的,所以会报错,而使用${}就不会出问题
动态设置表名 表名是不能加上单引号的
1 2 3 4 <select id ="getUserListByMe" resultType ="User" > select * from ${tableName} </select >
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @Test public void testGetUserListByMe () { SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.getSqlSession(); SpecialSQLMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(SpecialSQLMapper.class); List<User> t_user = mapper.getUserListByMe("t_user" ); t_user.forEach(System.out::println); }
获取自增的主键 1 2 3 4 5 void insertUserByMe (User user) ;
useGeneratedKeys 表示当前添加功能使用自增的主键
1 2 3 4 5 <insert id ="insertUserByMe" useGeneratedKeys ="true" keyProperty ="id" > insert into t_user values (null,#{username},#{password},#{age},#{gender},#{email}) </insert >
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @Test public void testInsertByMe () { SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.getSqlSession(); SpecialSQLMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(SpecialSQLMapper.class); User user = new User (null , "张三" , "010203" , 23 , "男" , "121@qq.com" ); mapper.insertUserByMe(user); System.out.println(user.getId()); }
此时就可以获取到user的id值:
自定义映射resultMap 这个就是设置那个驼峰映射
1 2 3 4 <settings > <setting name ="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value ="true" /> </settings >
这时新建两个表:t_emp和t_dept
emp_id
emp_name
age
gender
dept_id
dept_id
dept_name
当字段名和属性名不一致时,如何处理映射关系
为查询的字段设置别名,和Java中的属性名保持一致(为什么设置别名和Java中的一致就行了呢?因为设置了别名,查询出的结果就会以别名的形式列出来,这时与Java类中的属性名一致,MyBatis就可以接收到MySql查询出的结果)
当字段符合MySql的要求-使用的是下划线,而属性名符合Java的要求-使用驼峰
1 2 3 4 <settings > <setting name ="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value ="true" /> </settings >
就是把emp_id 映射为empId
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 <resultMap id ="empResultMap" type ="Emp" > <id column ="emp_id" property ="empId" > </id > <result column ="emp_name" property ="empName" > </result > <result column ="age" property ="age" > </result > <result column ="gender" property ="gender" > </result > </resultMap > <select id ="getEmpByEmpId" resultMap ="empResultMap" > select * from t_emp where emp_id = #{empId}; </select >
多对一的映射情况 又是三种方式:
直接使用resultMap处理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 <resultMap id ="empAndDeptResultMapOne" type ="Emp" > <id column ="emp_id" property ="empId" > </id > <result column ="emp_name" property ="empName" > </result > <result column ="age" property ="age" > </result > <result column ="gender" property ="gender" > </result > <result column ="dept_id" property ="dept.deptId" > </result > <result column ="dept_name" property ="dept.deptName" > </result > </resultMap >
处理了每个字段以及Dept中的属性对应关系,这里要注意dept_name和dept.deptId这种对应关系
使用association
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 <resultMap id ="empAndDeptResultMap" type ="Emp" > <id column ="emp_id" property ="empId" > </id > <result column ="emp_name" property ="empName" > </result > <result column ="age" property ="age" > </result > <result column ="gender" property ="gender" > </result > <association property ="dept" javaType ="Dept" > <id column ="dept_id" property ="deptId" > </id > <result column ="dept_name" property ="deptName" > </result > </association > </resultMap >
但是我说实话,这种实际上更麻烦了一点,但是比上一种看起来更清晰
分步查询
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 <resultMap id ="empAndDeptByStepResultMap" type ="Emp" > <id column ="emp_id" property ="empId" > </id > <result column ="emp_name" property ="empName" > </result > <result column ="age" property ="age" > </result > <result column ="gender" property ="gender" > </result > <association property ="dept" fetchType ="eager" select ="com.zzmr.mybatis.mapper.DeptMapper.getEmpAndDeptByStepTwo" column ="dept_id" > </association > </resultMap > <select id ="getEmpAndDeptByStepOne" resultMap ="empAndDeptByStepResultMap" > select * from t_emp where emp_id = #{empId}; </select > <select id ="getEmpAndDeptByStepTwo" resultType ="Dept" > select * from t_dept where dept_id = #{deptId}; </select >
将两个sql关联在一起就是在association标签中的select属性中,要关联方法名那就是,以后用到了来复制
但是问题也出现了,这个分步查询很明显比前面两种要麻烦很多,那它的优点是什么呢 延迟加载
1 2 3 4 <setting name ="lazyLoadingEnabled" value ="true" /> <setting name ="aggressiveLazyLoading" value ="false" />
设置了这两个标签后,就是全局配置了,而要想让某个分步查询还是立即加载的话,就可以在association标签中设置fetchType属性 当然,使用这个标签的前提是设置了全局配置
一对多的映射情况 一对多没有级联,只有collection标签和分步查询集合存储的类型 collection标签实现方式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 <resultMap id ="deptAndEmpResultMap" type ="Dept" > <id column ="dept_id" property ="deptId" > </id > <result column ="dept_name" property ="deptName" > </result > <collection property ="emps" ofType ="Emp" > <id column ="emp_id" property ="empId" > </id > <result column ="emp_name" property ="empName" > </result > <result column ="age" property ="age" > </result > <result column ="gender" property ="gender" > </result > </collection > </resultMap > <select id ="getDeptAndEmpByDeptId" resultMap ="deptAndEmpResultMap" > select * from t_dept LEFT JOIN t_emp on t_dept.dept_id = t_emp.dept_id where t_dept.dept_id = #{deptId}; </select >
分布查询
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 <resultMap id ="deptAndEmpResultMapByStep" type ="Dept" > <id column ="dept_id" property ="deptId" > </id > <result column ="dept_name" property ="deptName" > </result > <collection property ="emps" select ="com.zzmr.mybatis.mapper.EmpMapper.getDeptAndEmpByStepTwo" column ="dept_id" > </collection > </resultMap > <select id ="getDeptAndEmpByStepOne" resultMap ="deptAndEmpResultMapByStep" > select * from t_dept where dept_id = #{deptId}; </select >
在员工mapper中写上第二步查询
1 2 3 4 <select id ="getDeptAndEmpByStepTwoByMe" resultType ="Emp" > select * from t_emp where dept_id = #{deptId} </select >
当然对应的接口中都要有相应的抽象方法
动态Sql 就是根据特定条件去拼接Sql语句以实现某种效果
这里的主要问题就是Sql拼接时出现的bug,
使用where标签 就是会自动添加where关键字,如果后面的条件都不成立,则不会添加where关键字,还有去掉条件前的and关键字,但是不能去掉后面的and
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 <select id ="getEmpByCondition" resultType ="Emp" > select * from t_emp <where > <if test ="empName != null and empName != ''" > emp_name = #{empName} </if > <if test ="age != null and age != ''" > and age = #{age} </if > <if test ="gender != null and gender != ''" > and gender = #{gender} </if > </where > </select >
那如果以后用的话,就用where标签吧,感觉trim挺麻烦的,哈哈哈哈艹,就是要注意,第一个if里面不能加上and,其他就没啥了
trim标签 首先是trim标签的四个属性
使用prefix=”where”给sql添加where关键字
使用suffixOverrides=”and”自动删除语句后多余的and
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 <select id ="getEmpByCondition" resultType ="Emp" > select * from t_emp <trim prefix ="where" suffixOverrides ="and" > <if test ="empName != null and empName != ''" > emp_name = #{empName} and </if > <if test ="age != null and age != ''" > age = #{age} and </if > <if test ="gender != null and gender != ''" > gender = #{gender} </if > </trim > </select >
choose,when,otherwise标签 用的不多,但是要看得明白跟if.else.if.else很像 when最少设置一个,otherwise最多设置一个
若第一个when条件符合,那后面的情况都不会执行了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 <select id ="getEmpByChoose" resultType ="Emp" > select * from t_emp <where > <choose > <when test ="empName!=null and empName != ''" > emp_name = #{empName} </when > <when test ="age!=null and age!=''" > age = #{age} </when > <when test ="gender!=null and gender != ''" > gender = #{gender} </when > </choose > </where > </select >
比如这个,当测试里写上:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @Test public void testGetEmpByChoose () { SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.getSqlSession(); DynamicSQLMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(DynamicSQLMapper.class); Emp emp = new Emp (null , "张三" ,21 , "男" ); List<Emp> list = mapper.getEmpByChoose(emp); list.forEach(System.out::println); }
这时,因为第一个”张三”已经匹配上了,那后面的的21,还有”男”就没用了,因此现在执行完的结果是这样的,就算后面的不匹配(查询的是21,但实际上是20),也能查出来
forEach标签 这个标签还是很重要的,批量操作会用到separator属性 意为以什么字符分割
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 <insert id ="insertMoreEmp" > insert into t_emp values <foreach collection ="emps" item ="emp" separator ="," > (null,#{emp.empName},#{emp.age},#{emp.gender},null) </foreach > </insert >
这里要注意使用了Arrays.asList 方法,快速将一些项封装为一个集合
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @Test public void testInsertMoreEmp () { SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.getSqlSession(); DynamicSQLMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(DynamicSQLMapper.class); Emp emp1 = new Emp (null , "zzmr1" ,20 , "男" ); Emp emp2 = new Emp (null , "zzmr2" ,20 , "女" ); Emp emp3 = new Emp (null , "zzmr3" ,20 , "女" ); List<Emp> emps = Arrays.asList(emp1, emp2, emp3); mapper.insertMoreEmp(emps); }
还有批量删除的操作
1 2 3 4 5 6 <delete id ="deleteMoreEmp" > delete from t_emp where <foreach collection ="empIds" item ="empId" separator ="or" > emp_id = #{empId} </foreach > </delete >
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @Test public void testDeleteMoreEmp () { SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.getSqlSession(); DynamicSQLMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(DynamicSQLMapper.class); Integer[] emps = new Integer []{16 ,17 }; mapper.deleteMoreEmp(emps); }
还是非常方便的,只需要在Integer数组中写上要删除的id,就OK了
sql标签 还有一个标签叫sql标签
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 <sql id ="empColumns" > emp_id,emp_name,age,gender,dept_id </sql > <select id ="getEmpByCondition" resultType ="Emp" > select <include refid ="empColumns" > </include > from t_emp <trim prefix ="where" suffixOverrides ="and" > <if test ="empName != null and empName != ''" > emp_name = #{empName} and </if > <if test ="age != null and age != ''" > age = #{age} and </if > <if test ="gender != null and gender != ''" > gender = #{gender} </if > </trim > </select >
这个已讲完,后面就是重头戏了,缓存记得之前学的时候都没听懂
缓存 一级缓存 一级缓存就是通过同一个SqlSession查询到的数据,如果使用同一个SqlSession查询数据,此时会从缓存中直接获取一级缓存是默认开启的
一级缓存失效的情况
不同的SqlSession对应不同的一级缓存
同一个SqlSession但是查询条件不同
同一个SqlSession两次查询期间执行了任何一次增删改操作
同一个SqlSession两次查询期间手动清理了缓存
测试一
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 @Test public void testCacheByMe () { SqlSession sqlSession1 = SqlSessionUtil.getSqlSession(); SqlSession sqlSession2 = SqlSessionUtil.getSqlSession(); CacheMapper mapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(CacheMapper.class); CacheMapper mapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(CacheMapper.class); Emp emp1 = mapper1.getEmpByIdByMe(1 ); System.out.println(emp1); Emp emp2 = mapper1.getEmpByIdByMe(1 ); System.out.println(emp2); Emp emp3 = mapper2.getEmpByIdByMe(1 ); System.out.println(emp3); }
怎么感觉这块并不是很重要
测试条件三
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 @Test public void testCacheByMe () { SqlSession sqlSession1 = SqlSessionUtil.getSqlSession(); SqlSession sqlSession2 = SqlSessionUtil.getSqlSession(); CacheMapper mapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(CacheMapper.class); CacheMapper mapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(CacheMapper.class); Emp emp1 = mapper1.getEmpByIdByMe(1 ); System.out.println(emp1); mapper1.insertEmp(new Emp (null ,"zzmr" ,12 ,"男" )); Emp emp2 = mapper1.getEmpByIdByMe(1 ); System.out.println(emp2); }
测试条件4,两次查询期间手动清理了缓存 ,这个没啥说的吧,缓存都清理了,要重新查询也是很正常的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 @Test public void testCacheByMe () { SqlSession sqlSession1 = SqlSessionUtil.getSqlSession(); SqlSession sqlSession2 = SqlSessionUtil.getSqlSession(); CacheMapper mapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(CacheMapper.class); CacheMapper mapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(CacheMapper.class); Emp emp1 = mapper1.getEmpByIdByMe(1 ); System.out.println(emp1); sqlSession1.clearCache(); Emp emp2 = mapper1.getEmpByIdByMe(1 ); System.out.println(emp2); }
这可是要比笔记里写的清楚,每种测试都保留了,像笔记里我写的我都看不明白了
二级缓存 二级缓存时SqlSessionFactory级别的 ,通过同一个SqlSessionFactory创建的SqlSession查询的结果会被缓存,此后若查询相同的数据,结果就会从二级缓存中获取
在核心配置文件中,设置全局配置属性cacheEnabled=”true”,默认为true,不需要设置
在映射文件中设置 <cache/>
二级缓存必须在SqlSession关闭或提交之后有效 查询的数据所转换的实体类类型必须实现序列化的接口
使二级缓存失效的情况
刚搜了一下,都说MyBatis的缓存不建议使用,一级还可以,但是二级是不推荐使用的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 @Test public void testCache () throws IOException { InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml" ); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder ().build(is); SqlSession sqlSession1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true ); CacheMapper mapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(CacheMapper.class); Emp emp1 = mapper1.getEmpById(1 ); System.out.println(emp1); mapper1.insertEmp(new Emp (null ,"zzmr" ,12 ,"男" )); sqlSession1.close(); SqlSession sqlSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true ); CacheMapper mapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(CacheMapper.class); Emp emp2 = mapper2.getEmpById(1 ); System.out.println(emp2); sqlSession2.close(); }
这时就能验证二级缓存
但别忘了还有第4个条件,”查询的数据所转换的实体类类型必须实现序列化的接口”
1 public class Emp implements Serializable
这时运行的日志里会有一个Cache Hit Ratio ,也就是缓存命中率,只要不为零,那就是从缓存中获取的数据只有二级缓存才会输出缓存命中率
二级缓存相关配置
evlction属性: 缓存回收策略,默认是LRU
LRU(Least Recently Used) 最近最少使用的:移除最长时间不被使用的对象
FiFO(First in First out) 先进先出:按对象进入缓存的顺序来移除它们
SOFT 软引用: 移除基于垃圾收集器状态的弱引用规则的对象
WEAK 弱引用: 更积极地移除基于垃圾收集器状态的弱引用规则的对象
flushinterval属性: 刷新间隔,单位毫秒,默认情况是不设置,也就是没有刷新间隔,缓存仅仅调用语句时刷新
size属性: 引用数目,正整数 代表缓存最多可以存储多少个对象,太大容易导致内存溢出
readOnly属性,只读,true/false
true 只读缓存,会给所有调用者返回缓存对象的相同实例,因此这些对象不能被修改,者提供了很重要的性能优势
false 读写缓存,会返回缓存对象的拷贝(通过序列化),这回满一下,但是安全,因此默认是false
MyBatis缓存查询顺序 SqlSession关闭之后,一级缓存中的数据会写入二级缓存
整合第三方缓存 说实话感觉没用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 <dependency > <groupId > org.mybatis.caches</groupId > <artifactId > mybatis-ehcache</artifactId > <version > 1.2.1</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > ch.qos.logback</groupId > <artifactId > logback-classic</artifactId > <version > 1.2.3</version > </dependency >
还有一个配置文件,同样放在resources目录下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <ehcache xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation ="../config/ehcache.xsd" > <diskStore path ="D:\zzmr\ehcache" /> <defaultCache maxElementsInMemory ="1000" maxElementsOnDisk ="10000000" eternal ="false" overflowToDisk ="true" timeToIdleSeconds ="120" timeToLiveSeconds ="120" diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds ="120" memoryStoreEvictionPolicy ="LRU" > </defaultCache > </ehcache >
在mapper映射文件中加入
1 <cache type ="org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache" />
还有logback.xml日志配置文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <configuration debug ="true" > <appender name ="STDOUT" class ="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender" > <encoder > <pattern > [%d{HH:mm:ss.SSS}] [%-5level] [%thread] [%logger] [%msg]%n</pattern > </encoder > </appender > <root level ="DEBUG" > <appender-ref ref ="STDOUT" /> </root > <logger name ="com.zzmr.mybatis.mapper" level ="DEBUG" /> </configuration >
总结一句话,以后用缓存就用redis了,而这些用不到
逆向工程 逆向工程:创建好数据表,然后再生成java类
精简版 pom.xml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 <dependencies > <dependency > <groupId > org.mybatis</groupId > <artifactId > mybatis</artifactId > <version > 3.5.7</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > junit</groupId > <artifactId > junit</artifactId > <version > 4.12</version > <scope > test</scope > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > log4j</groupId > <artifactId > log4j</artifactId > <version > 1.2.17</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > mysql</groupId > <artifactId > mysql-connector-java</artifactId > <version > 8.0.16</version > </dependency > </dependencies > <build > <plugins > <plugin > <groupId > org.mybatis.generator</groupId > <artifactId > mybatis-generator-maven-plugin</artifactId > <version > 1.3.0</version > <dependencies > <dependency > <groupId > org.mybatis.generator</groupId > <artifactId > mybatis-generator-core</artifactId > <version > 1.3.2</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > mysql</groupId > <artifactId > mysql-connector-java</artifactId > <version > 8.0.16</version > </dependency > </dependencies > </plugin > </plugins > </build >
MyBatis的核心配置文件还是那几个,这玩意不影响逆向工程的配置,所以不用放里面了
generatorConfig.xml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE generatorConfiguration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD MyBatis Generator Configuration 1.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-generator-config_1_0.dtd" > <generatorConfiguration > <context id ="DB2Tables" targetRuntime ="MyBatis3Simple" > <jdbcConnection driverClass ="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" connectionURL ="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm?serverTimezone=UTC" userId ="root" password ="010203" > </jdbcConnection > <javaModelGenerator targetPackage ="com.zzmr.mybatis.pojo" targetProject =".\src\main\java" > <property name ="enableSubPackages" value ="true" /> <property name ="trimStrings" value ="true" /> </javaModelGenerator > <sqlMapGenerator targetPackage ="com.zzmr.mybatis.mapper" targetProject =".\src\main\resources" > <property name ="enableSubPackages" value ="true" /> </sqlMapGenerator > <javaClientGenerator type ="XMLMAPPER" targetPackage ="com.zzmr.mybatis.mapper" targetProject =".\src\main\java" > <property name ="enableSubPackages" value ="true" /> </javaClientGenerator > <table tableName ="t_emp" domainObjectName ="Emp" /> <table tableName ="t_dept" domainObjectName ="Dept" /> </context > </generatorConfiguration >
配置文件写好之后就可以跑起来了
点击右上角的maven,找到该模块,点击Plugins,找到mybatis-generator
然后代码就自动生成了
然后我就是测试啊toString方法没有重写 toString方法吗 有参构造 也没有自动生成,这个简洁版有点太简洁了啊
还真是
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 import com.zzmr.mybatis.mapper.EmpMapper;import com.zzmr.mybatis.pojo.Emp;import com.zzmr.mybatis.utils.SqlSessionUtil;import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;import org.junit.Test;import java.util.List;public class SimpleTest { @Test public void testDeleteByPrimaryKey () { SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.getSqlSession(); EmpMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpMapper.class); int i = mapper.deleteByPrimaryKey(22 ); System.out.println(i); } @Test public void testInsert () { SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.getSqlSession(); EmpMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpMapper.class); Emp emp = new Emp (null ,"zzmr" ,20 ,"男" ,1 ); int i = mapper.insert(emp); System.out.println(i); } @Test public void testSelectPrimaryKey () { SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.getSqlSession(); EmpMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpMapper.class); Emp emp = mapper.selectByPrimaryKey(1 ); System.out.println(emp); } @Test public void testSelectAll () { SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.getSqlSession(); EmpMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpMapper.class); List<Emp> emps = mapper.selectAll(); emps.forEach(System.out::println); } @Test public void testUpdateByPrimaryKey () { SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.getSqlSession(); EmpMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpMapper.class); Emp emp = new Emp (23 ,"杨晋" ,20 ,"男" ,1 ); int i = mapper.updateByPrimaryKey(emp); System.out.println(i); } }
把生成的所有方法都测试一遍了,应该没啥问题,看看后面那个什么完整版啊
没有重写有参构造,toString方法
只能单表查询,不能多表联查
完整版 只需要把generatorConfig.xml中的MyBatis3Simple改成MyBatis3就好了
说人话就是,同样的操作可以使用的方法更多了,也更完整了
完整版生成的实体类也是没有toString方法的
还要注意自己在实体类中写上有参/无参构造
选择性修改,就是当修改时没有修改某个字段时,是不会动该字段的,而普通修改,就会全部覆盖
而这个selectByExample方法,要先创建Example对象,然后给这个对象添加条件可以添加的条件贼多
测试晚上跑完步回来再测
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 package com.zzmr.mybatis.test;import com.zzmr.mybatis.mapper.EmpMapper;import com.zzmr.mybatis.pojo.Emp;import com.zzmr.mybatis.pojo.EmpExample;import com.zzmr.mybatis.utils.SqlSessionUtil;import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;import org.junit.Test;import java.util.List;public class CompleteTest { @Test public void testCountByExample () { SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.getSqlSession(); EmpMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpMapper.class); EmpExample example = new EmpExample (); example.createCriteria().andEmpNameEqualTo("张三" ); int i = mapper.countByExample(example); System.out.println(i); } @Test public void testDeleteByExample () { SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.getSqlSession(); EmpMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpMapper.class); EmpExample example = new EmpExample (); example.createCriteria().andAgeEqualTo(12 ); int i = mapper.deleteByExample(example); System.out.println(i); } @Test public void testDeleteByPrimaryKey () { SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.getSqlSession(); EmpMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpMapper.class); int i = mapper.deleteByPrimaryKey(23 ); System.out.println(i); } @Test public void testInsert () { SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.getSqlSession(); EmpMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpMapper.class); Emp emp = new Emp (null ,"ZZMR123" ,20 ,"男" ); int i = mapper.insert(emp); System.out.println(i); } @Test public void testInsertSelective () { SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.getSqlSession(); EmpMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpMapper.class); int insert = mapper.insertSelective(new Emp (null , "ZZMR1" , null , null , null )); System.out.println(insert); } @Test public void testSelectByExample () { SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.getSqlSession(); EmpMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpMapper.class); EmpExample example = new EmpExample (); example.createCriteria().andEmpNameEqualTo("张三" ).andGenderEqualTo("女" ); example.or().andAgeGreaterThan(26 ); List<Emp> emps = mapper.selectByExample(example); emps.forEach(System.out::println); } @Test public void testSelectByPrimaryKey () { SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.getSqlSession(); EmpMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpMapper.class); Emp emp = mapper.selectByPrimaryKey(1 ); System.out.println(emp); } @Test public void testUpdateByPrimaryKey () { SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.getSqlSession(); EmpMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpMapper.class); Emp emp = new Emp (23 ,"ZZMR" ,20 ,null ); mapper.updateByPrimaryKey(emp); } @Test public void testUpdateByPrimaryKeySelective () { SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.getSqlSession(); EmpMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpMapper.class); Emp emp = new Emp (23 ,"ZZMR1" ,20 ,null ); mapper.updateByPrimaryKeySelective(emp); } }
分页插件 依稀记得这个是真的难
配置分页插件 先加依赖
1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > com.github.pagehelper</groupId > <artifactId > pagehelper</artifactId > <version > 5.2.0</version > </dependency >
在MyBatis核心配置文件中添加插件
1 2 3 4 <plugins > <plugin interceptor ="com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor" > </plugin > </plugins >
要注意插件放的位置,这个标签要放在environments标签上面
而使用的步骤也很简单在查询之前开启分页功能
1 Page{count=true , pageNum=1 , pageSize=4 , startRow=0 , endRow=4 , total=32 , pages=8 , reasonable=false , pageSizeZero=false }[Emp{empId=1 , empName='1' , age=null , gender='null' }, Emp{empId=2 , empName='23' , age=null , gender='null' }, Emp{empId=3 , empName='4' , age=null , gender='null' }, Emp{empId=4 , empName='45' , age=null , gender='null' }]
还有一个pageInfo对象
1 PageInfo<Emp> pageInfo = new PageInfo <>(emps,5 );
这个里面也很多数据,比page中的数据还要多
1 2 3 4 5 PageInfo{ pageNum=1 , pageSize=4 , size=4 , startRow=1 , endRow=4 , total=32 , pages=8 , list=Page{ count=true , pageNum=1 , pageSize=4 , startRow=0 , endRow=4 , total=32 , pages=8 , reasonable=false , pageSizeZero=false } [Emp{empId=1 , empName='1' , age=null , gender='null' }, Emp{empId=2 , empName='23' , age=null , gender='null' }, Emp{empId=3 , empName='4' , age=null , gender='null' }, Emp{empId=4 , empName='45' , age=null , gender='null' }], prePage=0 , nextPage=2 , isFirstPage=true , isLastPage=false , hasPreviousPage=false , hasNextPage=true , navigatePages=5 , navigateFirstPage=1 , navigateLastPage=5 , navigatepageNums=[1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ]}
这个pageInfo对象里面存的数据是真的多啊
Spring 这几天忙着打游戏,忙着写人工智能实验(虽然写不明白),嗯,2022年10月22日 15点57分
IOC容器 Inversion of Control 反转控制
实现 看图吧,东西有点多,但是又不多
用的比较多的就是ClassPathXmlApplicationContext类
基于XML管理bean 这里就要强调了,一共两种管理方式,基于XML和基于注解,两种都非常重要,以后都会用到
流程是什么?
Java类
Spring配置文件-applocationContext.xml
1 <bean id ="helloworld" class ="com.zzmr.spring.pojo.HelloWorld" > </bean >
这时,IOC容器中就可以获取到HelloWorld类了,id为helloworld
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @Test public void testHelloWorld () { ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ("applicationContext.xml" ); HelloWorld helloworld = (HelloWorld) ioc.getBean("helloworld" ); helloworld.sayHello(); }
内容突然就多起来了IOC容器获取对象实际上是根据反射实现的,这时就必须要要求Bean类有无参构造,没有的话就会出错
下面看获取Bean的三种方式
根据id获取,这个就是上面写的那种
根据bean的类型获取要求该IOC容器中有且只有一个类型匹配的bean
1 Student studentOne = ioc.getBean(Student.class);
根据bean的id和类型获取
1 Student studentOne = ioc.getBean("studentOne" , Student.class);
两个都用上了属于是,
那以后用什么获取方式比较多呢,用根据类型获取
组件类实现了接口,根据接口类型可以获取bean,前提是bean唯一
依赖注入之setter注入 就是那个DI
说白了,依赖注入就是给类中的某些属性赋值的过程-也是写bean
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 <bean id ="studentTwo" class ="com.zzmr.spring.pojo.Student" > <property name ="sid" value ="1001" > </property > <property name ="sname" value ="张三" > </property > <property name ="age" value ="23" > </property > <property name ="gender" value ="男" > </property > </bean >
这个”依赖注入”,写上参数之后,再次使用IOC容器来获取该类的对象时,就会获取注入后的对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @Test public void testIOCByMe () { ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ("spring-ioc.xml" ); Student studentTwo = ioc.getBean("studentTwo" , Student.class); System.out.println(studentTwo); }
依赖注入之构造器注入
这个就是使用类的构造方法来实现成员变量的赋值的这里要注意,如果使用构造器注入,因为是使用了构造方法,所以里面的每个属性的顺序要和构造方法一致,不一致就会出现类型不匹配的问题
1 2 3 4 5 6 <bean id ="studentThree" class ="com.zzmr.spring.pojo.Student" > <constructor-arg value ="1002" > </constructor-arg > <constructor-arg value ="李四" > </constructor-arg > <constructor-arg value ="女" > </constructor-arg > <constructor-arg value ="24" > </constructor-arg > </bean >
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @Test public void testIOCByMe () { ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ("spring-ioc.xml" ); Student studentThree = ioc.getBean("studentThree" , Student.class); System.out.println(studentThree); }
要注意的地方,如果出现两个构造方法,而某个参数不同,但参数的类型相同,这时可以指定使用哪一个构造方法,需要用到name属性
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public Student (Integer sid, String sname, String gender,Double score) { this .sid = sid; this .sname = sname; this .gender = gender; this .score = score; } public Student (Integer sid, String sname, String gender,Integer age) { this .sid = sid; this .sname = sname; this .gender = gender; this .age = age; }
此时就可以使用name属性来指定了
1 2 3 4 5 6 <bean id ="studentThree" class ="com.zzmr.spring.pojo.Student" > <constructor-arg value ="1002" > </constructor-arg > <constructor-arg value ="李四" > </constructor-arg > <constructor-arg value ="女" > </constructor-arg > <constructor-arg value ="24" name ="score" > </constructor-arg > </bean >
使用name指定这个arg是给哪个属性赋值—给score赋值
以上两种方式哪种用的多?当然是第一种,使用property赋值
特殊值处理 为属性赋值为null 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 <bean id ="studentFour_two" class ="com.zzmr.spring.pojo.Student" > <property name ="sid" value ="1003" > </property > <property name ="sname" value ="王五" > </property > <property name ="gender" > <null > </null > </property > <property name ="age" value ="23" > </property > </bean >
是不能直接在value里写上null的,不然会变成字符串null,正确的方法是在property标签中写上null标签,此时就对应gender为null,为空
xml实体 这里要记住大于号和小于号
1 2 3 4 5 6 <bean id ="studentFour_three" class ="com.zzmr.spring.pojo.Student" > <property name ="sid" value ="1003" > </property > <property name ="sname" value ="<王五>" > </property > <property name ="gender" value ="男" > </property > <property name ="age" value ="23" > </property > </bean >
CD区
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 <bean id ="studentFour_three" class ="com.zzmr.spring.pojo.Student" > <property name ="sid" value ="1003" > </property > <property name ="sname" > <value > <![CDATA[<王五>]]></value > </property > <property name ="gender" value ="男" > </property > <property name ="age" value ="23" > </property > </bean >
为类类型属性赋值 第一种方式:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 <bean id ="studentFive_two" class ="com.zzmr.spring.pojo.Student" > <property name ="sid" value ="1004" > </property > <property name ="sname" value ="赵六" > </property > <property name ="age" value ="14" > </property > <property name ="gender" value ="男" > </property > <property name ="clazz" ref ="clazzTwo" > </property > </bean > <bean id ="clazzTwo" class ="com.zzmr.spring.pojo.Clazz" > <property name ="cid" value ="123" > </property > <property name ="cname" value ="高一一班" > </property > </bean >
也没什么难的,主要是要给类类型的属性单独写一个bean,然后用ref来引用即可
第二种方式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 <bean id ="clazzTwo" class ="com.zzmr.spring.pojo.Clazz" > <property name ="cid" value ="123" > </property > <property name ="cname" value ="高一一班" > </property > </bean > <bean id ="studentFive_three" class ="com.zzmr.spring.pojo.Student" > <property name ="sid" value ="1004" > </property > <property name ="sname" value ="赵六" > </property > <property name ="age" value ="14" > </property > <property name ="gender" value ="男" > </property > <property name ="clazz" ref ="clazzTwo" > </property > <property name ="clazz.cid" value ="123" > </property > <property name ="clazz.cname" value ="高二二班" > </property > </bean >
哪个用的多?是第一种引用外部的bean,还有就是使用内部的bean,而级联这种方式用的不多
第三种-使用内部bean
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 <bean id ="studentFive_four" class ="com.zzmr.spring.pojo.Student" > <property name ="sid" value ="1004" > </property > <property name ="sname" value ="赵六" > </property > <property name ="age" value ="14" > </property > <property name ="gender" value ="男" > </property > <property name ="clazz" > <bean id ="clazzInner" class ="com.zzmr.spring.pojo.Clazz" > <property name ="cid" value ="123" > </property > <property name ="cname" value ="高一二班" > </property > </bean > </property > </bean >
这里要注意的是,内部bean只能在这个类中使用,在IOC是无法直接获取该bean的
为数组类型属性赋值
这里要注意使用的是array标签,也是使用的内部bean
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 <bean id ="studentFive_five" class ="com.zzmr.spring.pojo.Student" > <property name ="sid" value ="1004" > </property > <property name ="sname" value ="赵六" > </property > <property name ="age" value ="14" > </property > <property name ="gender" value ="男" > </property > <property name ="clazz" > <bean id ="clazzInner" class ="com.zzmr.spring.pojo.Clazz" > <property name ="cid" value ="123" > </property > <property name ="cname" value ="高一二班" > </property > </bean > </property > <property name ="hobby" > <array > <value > 抽烟</value > <value > 喝酒</value > <value > 烫头</value > <value > 学习</value > </array > </property > </bean >
为集合类型赋值 也不难
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 <bean id ="clazzThree" class ="com.zzmr.spring.pojo.Clazz" > <property name ="cid" value ="123" > </property > <property name ="cname" value ="高三三班" > </property > <property name ="students" > <list > <ref bean ="studentOne" > </ref > <ref bean ="studentTwo" > </ref > <ref bean ="studentThree" > </ref > </list > </property > </bean >
测试:
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Test public void testIOCByMeTwo () { ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ("spring-ioc.xml" ); Clazz clazz = ioc.getBean("clazzThree" , Clazz.class); System.out.println(clazz); }
结果:
配置一个集合类型的bean,需要使用util约束
1 2 3 4 5 6 <util:list id ="studentList" > <ref bean ="studentOne" > </ref > <ref bean ="studentTwo" > </ref > <ref bean ="studentThree" > </ref > </util:list >
使用时,只需要引用即可
1 2 3 4 5 <bean id ="clazzThree" class ="com.zzmr.spring.pojo.Clazz" > <property name ="cid" value ="123" > </property > <property name ="cname" value ="高三三班" > </property > <property name ="students" ref ="studentList" > </property > </bean >
为map集合类型的属性赋值 用起来也没什么难的
设置teacher的bean
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 <bean id ="teacherOne" class ="com.zzmr.spring.pojo.Teacher" > <property name ="tid" value ="10084" > </property > <property name ="tname" value ="名字1" > </property > </bean > <bean id ="teacherTwo" class ="com.zzmr.spring.pojo.Teacher" > <property name ="tid" value ="100844" > </property > <property name ="tname" value ="名字二" > </property > </bean >
使用map
1 2 3 4 5 6 <property name ="teacherMap" > <map > <entry key ="10084" value-ref ="teacherOne" > </entry > <entry key ="100844" value-ref ="teacherTwo" > </entry > </map > </property >
第二种方式:
1 2 3 4 <util:map id ="teacherMapTwo" > <entry key ="10084" value-ref ="teacherOne" > </entry > <entry key ="100844" value-ref ="teacherTwo" > </entry > </util:map >
使用时:
1 <property name ="teacherMap" ref ="teacherMapTwo" > </property >
p命名空间 这个没啥说的,用的也不多
1 2 3 <bean id ="studentSix" class ="com.zzmr.spring.pojo.Student" p:sid ="1005" p:sname ="小明" p:teacherMap-ref ="teacherMap" > </bean >
Spring管理数据源 添加依赖-mysql驱动和数据库连接池(数据源)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 <dependency > <groupId > mysql</groupId > <artifactId > mysql-connector-java</artifactId > <version > 8.0.16</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > com.alibaba</groupId > <artifactId > druid</artifactId > <version > 1.0.31</version > </dependency >
实现:
还有就是这个property可以设置一些数据库连接池的属性,总之就是mybatis配置文件中能设置的,spring也都能设置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 <context:property-placeholder location ="jdbc.properties" > </context:property-placeholder > <bean id ="dataSource" class ="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" > <property name ="driverClassName" value ="${jdbc.driver}" > </property > <property name ="url" value ="${jdbc.url}" > </property > <property name ="username" value ="${jdbc.username}" > </property > <property name ="password" value ="${jdbc.password}" > </property > </bean >
测试一下
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Test public void testDataSource () throws SQLException { ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ("spring-datasource.xml" ); DruidDataSource data = ioc.getBean(DruidDataSource.class); System.out.println(data.getConnection()); }
能输出一串地址就行,就证明获取成功
上面需要注意的就是一个context:property-placeholder标签,负责引入jdbc.properties文件,以后引入properties文件全是用的这个标签
bean的作用域 说是作用域,但是感觉更像是bean给创建Java对象指定的类型
单例和多例的区别:单例,表示获取该bean所对应的对象都是同一个,多例,表示获取该bean所对应的对象都不是同一个一般都是使用单例,多例使用的不多
1 2 3 4 5 <bean id ="student" class ="com.zzmr.spring.pojo.Student" scope ="singleton" > <property name ="sid" value ="2009124101" > </property > <property name ="sname" value ="杨晋" > </property > </bean >
测试类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @Test public void testScope () { ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ("spring-scope.xml" ); Student student1 = ioc.getBean(Student.class); Student student2 = ioc.getBean(Student.class); System.out.println(student1==student2); }
bean生命周期 感觉也没什么看的
实例化-调用无参构造
依赖注入-调用set方法
初始化-调用initMethod()方法,方法名是自定义的
销毁(使用后销毁)-调用destoryMethod()方法,方法名是自定义的
要在bean标签中写上destoryMethod属性
代码啥的看原来的笔记
IOC容器创建时就会创建bean,而不是获取bean时才创建对象-前提是默认为单例,如果修改为多例prototype,这时创建IOC容器并不会创建bean对象,要在获取bean时才会创建对象-执行三个步骤
后置处理器配置完,IOC容器中所有的bean都会有这个功能
配置:
1 <bean id ="myBeanPostProcessor" class ="com.zzmr.spring.process.MyBeanPostProcessor" > </bean >
方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 package com.zzmr.spring.process;import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization (Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { System.out.println("MyBeanPostProcessor---->后置处理器的postProcessBeforeInitialization" ); return bean; } @Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization (Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { System.out.println("MyBeanPostProcessor---->后置处理器的postProcessAfterInitialization" ); return bean; } }
上面这两个抽象方法不重写是不会报红的,这也说明:方法有默认的方法体或者用static静态修饰了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 @Nullable default Object postProcessBeforeInitialization (Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { return bean; } @Nullable default Object postProcessAfterInitialization (Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { return bean; }
FactoryBean
一句话总结,配置FactoryBean类型的bean,在获取bean(getBean)时得到的不是class属性,而是geObject()方法的返回值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 package com.zzmr.spring.factory;import com.zzmr.spring.pojo.User;import org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean;public class UserFactoryBean implements FactoryBean <User> { @Override public User getObject () throws Exception { return new User (); } @Override public Class<?> getObjectType() { return User.class; } }
配置FactoryBean
1 <bean class ="com.zzmr.spring.factory.UserFactoryBean" />
测试:
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Test public void testFactoryBean () { ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ("spring-factory.xml" ); User user = ioc.getBean(User.class); System.out.println(user); }
这个时候就不用单独配置UserBean了,FactoryBean直接代替了这种形式,以后Spring整合MyBatis也是使用的这种方式
基于xml的自动装配
自动装配,这块就是很重要的了刚才回顾了一下之前写的书城book项目,算不上项目吧,终于能跑起来了,原来是少了一个jar包,导入那个jar包就ok了
那个B三层架构,Controller层调用service层,service层调用dao层,dao和数据库进行交互
先看看手动装配,不是啊,是原始方式引用外部bean
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 <bean id ="userController" class ="com.zzmr.spring.controller.UserController" > <property name ="userService" ref ="userService" > </property > </bean > <bean id ="userService" class ="com.zzmr.spring.service.impl.UserServiceImpl" > <property name ="userDao" ref ="userDao" > </property > </bean > <bean id ="userDao" class ="com.zzmr.spring.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl" > </bean >
测试:
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Test public void testAutowire () { ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ("spring-autowire-xml.xml" ); UserController userController = ioc.getBean(UserController.class); userController.saveUser(); }
自动装配
autowire属性设置自动装配的策略
no,default表示不装配,就相当于没有配置
byType,根据类型,在controller的bean中配置时,相当于会自动装配service,就是Controller中用到service时,ioc容器会自动匹配对应类型的bean(service),此时就能实现自动装配的效果
byName,根据属性名,当一个类对应的bean有多个时,就可以用到byName,当然,谁没事会把一个类配置多个bean
下面是byType的演示
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 <bean id ="userController" class ="com.zzmr.spring.controller.UserController" autowire ="byType" > </bean > <bean id ="userService" class ="com.zzmr.spring.service.impl.UserServiceImpl" autowire ="byType" > </bean > <bean id ="userDao" class ="com.zzmr.spring.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl" > </bean >
注意:
基于注解管理bean
给类和属性加上注解(标记)
在配置文件中扫描组件
4个常用注解
@Component:将类标识为普通组件这四个注解,功能是一模一样的,是为了便于程序员区分才写成这样
扫描 1 <context:component-scan base-package ="com.zzmr.spring" > </context:component-scan >
没啥复杂的,主要是一些细节要记住说的直白一点,就是一个类加了上面的注解,那这个类在ioc容器中就有了对应的bean
这个怎么说呢,可以通过接口获取bean,但是给一个实现类设置了bean的话,就会出现找不到匹配的类,会把实现类和接口都找出来,就很奇怪,不知道怎么了就出现了这个bug,又不知道咋了这个bug就没了,奇怪
还要注意一个事
以后SpringMVC要扫描的是控制层,而Spring要扫描除了控制层以外的所有组件
spring扫描排除控制层:
根据注解来排除-annotation
1 2 3 4 <context:component-scan base-package ="com.zzmr.spring" > <context:exclude-filter type ="annotation" expression ="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller" /> </context:component-scan >
这样就可以实现排除掉控制层了
根据类型来排除-assignable只需要把全类名写在expression中就行
1 2 3 4 <context:component-scan base-package ="com.zzmr.spring" > <context:exclude-filter type ="assignable" expression ="com.zzmr.spring.controller.UserController" /> </context:component-scan >
以后用哪个多?用第一个根据注解排除比较多,因为等到SSM整合时,Spring负责扫描除了控制层之外的所有类型,而控制层会有很多类,此时一个一个排除很麻烦,并没有直接用注解排除方便
包含的,我感觉就没必要写了前提是在context-component-scan标签中设置use-default-filters=”false” ,因为扫描标签默认是扫描整个包的,都扫描整个包了,再设置一个包含,也没什么意义,所以要把默认扫描整个包给关了,就可以实现只扫描特定的包了
同样是根据注解包含:
1 2 3 4 <context:component-scan base-package ="com.zzmr.spring" use-default-filters ="false" > <context:include-filter type ="annotation" expression ="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller" /> </context:component-scan >
根据类型包含:
1 2 3 4 <context:component-scan base-package ="com.zzmr.spring" use-default-filters ="false" > <context:include-filter type ="assignable" expression ="com.zzmr.spring.controller.UserController" /> </context:component-scan >
bean的id通过注解+扫描所配置的bean的id,默认值为类的小驼峰,即类型的首字母为小写的结果
获取测试
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @Test public void testByMe () { ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ("spring-ioc-annotation.xml" ); UserController userController = ioc.getBean("userController" ,UserController.class); System.out.println(userController); UserService userService = ioc.getBean("userServiceImpl" ,UserService.class); System.out.println(userService); UserDao userDao = ioc.getBean("userDaoImpl" ,UserDao.class); System.out.println(userDao); }
还可以自定义名字
1 2 @Controller("userControllerByTest") public class UserController {}
当然某些特殊情况还是会用到的,比如在SpringMVC中使用的文件上传解析器,就必须设置id
基于注解的自动装配 原来笔记写的是个啥啊,一坨屎
直接拿例子说话,基于注解的自动装配,首先就是要用到@Autowired,比如,要在Controller中创建Service对象,之前是在xml中的bean中实现自动装配的,而现在是根据注解实现,所以要在声明Service对象时加上@Autowired注解:
1 2 @Autowired private UserService userService;
之前拿xml实现自动装配时要求必须有set方法,而基于注解实现就不需要有set方法了
@AutoWired能够标识的位置
标识在成员变量上-此时不需要设置成员变量的set方法(老师推荐的)
标识在set方法上
标识在为当前成员变量赋值的有参构造上
@Autowired注解的原理
byType还是byName?肯定是byType,或者说默认是byType,因为这个注解是加在成员变量service上的,而ioc管理的bean是service的实现类-serviceImpl,名字都不匹配,byName是找不到的,所以@Autowired注解的默认实现是byType
如果有多个类型匹配的bean,此时会自动转换为byName的方式实现自动装配
若byType和byName的方式都无法实现自动装配,即IOC容器中有多个类型匹配的bean,且这些bean的id和要赋值的属性的属性名都不一致,此时会抛出异常-NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException,此时可以在要赋值的属性上,添加一个@Qualifier(“”)注解,然后括号里指定上某一个bean的id,来赋值就好了
但上面的情况会出现吗,很小的几率吧,哪有byType不行,byName又不行的哈哈哈哈哈以后的用法就是,在每个层上加上该有的注解,然后在需要赋值的成员变量上加上@Autowired注解,其他啥都不需要啊哈哈哈
特殊的情况
@Autowired注解有一个required属性,默认是true,要求必须完成自动装配,设置成false,此时能装配则装配,不能装配则使用默认值
IOC终于看完了!
AOP 场景模拟 模拟什么,就是模拟一个程序,这个程序里有一些非连续执行的代码,这些代码也不是核心代码,但是就是必须要用,比如:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @Override public int add (int i, int j) { System.out.println("日志:方法名:add 参数:" + i + "," + j); int result = i + j; System.out.println("方法内部, result:" + result); System.out.println("日志:方法名:add 结果:" + result); return result; }
像里面的两行日志代码,一个方法里就需要写上两个,四个方法就需要写上八个,而且由于是非连续执行的代码,也不能像JDBCUtils一样封装
问题就出现了,比如现在要去更改日志的格式,那就要去更改所有使用到地方,这就导致维护成本大大增加
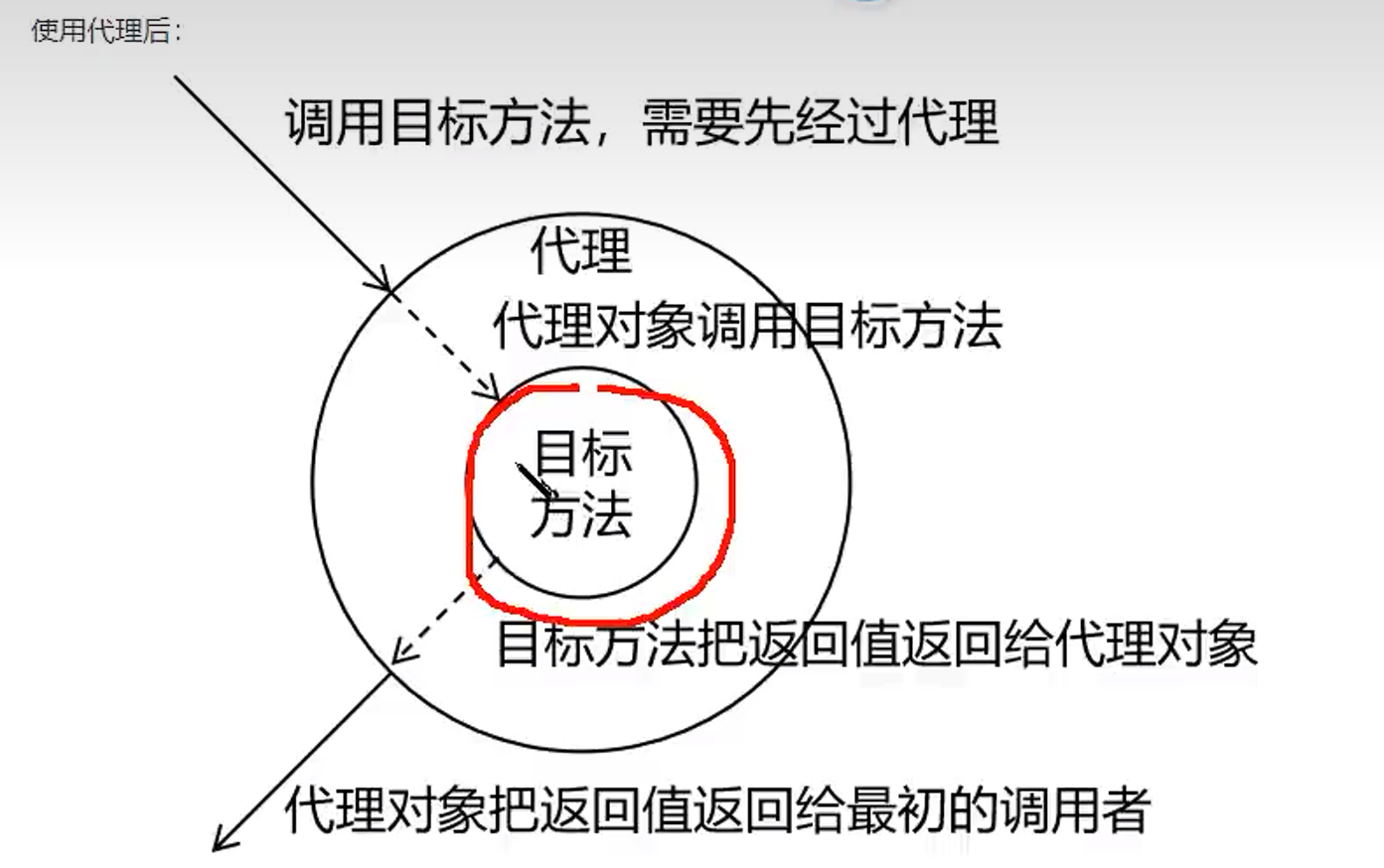
引入”代理”
使用代理后:
这次算是明白了,相当于什么呢
静态代理 静态代理还是很简单的 这还是要注意一点,代理类要和目标类实现相同的接口
此时的目标方法(被代理的)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 package com.zzmr.spring.proxy;public class CalculatorByMeImpl implements CalculatorByMe { @Override public int add (int i, int j) { int result = i + j; System.out.println("方法内部, result:" + result); return result; } @Override public int sub (int i, int j) { int result = i - j; System.out.println("方法内部, result:" + result); return result; } @Override public int mul (int i, int j) { int result = i * j; System.out.println("方法内部, result:" + result); return result; } @Override public int div (int i, int j) { int result = i / j; System.out.println("方法内部, result:" + result); return result; } }
代理类:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 package com.zzmr.spring.proxy;public class CalculatorStaticProxyByMe implements CalculatorByMe { private CalculatorByMeImpl target; public CalculatorStaticProxyByMe (CalculatorByMeImpl target) { this .target = target; } @Override public int add (int i, int j) { System.out.println("日志,方法名:add, 参数:" + i + "," + j); int result = target.add(i, j); System.out.println("日志,结果:result,:" + result); return result; } @Override public int sub (int i, int j) { System.out.println("日志,方法名:sub, 参数:" + i + "," + j); int result = target.sub(i, j); System.out.println("日志,结果:result,:" + result); return result; } @Override public int mul (int i, int j) { System.out.println("日志,方法名:mul, 参数:" + i + "," + j); int result = target.mul(i, j); System.out.println("日志,结果:result,:" + result); return result; } @Override public int div (int i, int j) { System.out.println("日志,方法名:div, 参数:" + i + "," + j); int result = target.div(i, j); System.out.println("日志,结果:result,:" + result); return result; } }
测试:
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Test public void testByProxy () { CalculatorStaticProxyByMe cal = new CalculatorStaticProxyByMe (new CalculatorByMeImpl ()); int result = cal.sub(1 , 2 ); System.out.println(result); }
这里要创建的是代理对象,而不是目标对象
此时还可以增加代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 @Override public int add (int i, int j) { int result = 0 ; try { System.out.println("日志,方法名:add, 参数:" + i + "," + j); result = target.add(i, j); System.out.println("日志,结果:result,:" + result); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("日志:出现异常" ); } finally { } return result; }
所以说静态代理确实实现了解耦,但是由于代码都是写死了,完全不具备任何的灵活性,就拿日志功能来说,将来其他地方也需要附加日志,那还得再声明更多个静态代理类,那就产生了大量重复的代码,日志功能还是分散的,没有统一管理
动态代理 这里引入Proxy类,以及Proxy.newProxyInstance(),里面有三个参数,第一个ClassLoader类加载器,你还记得类加载器是什么吗
ClassLoader loader 指定加载动态生成的代理类的类加载器 只需要获取某个类型的class对象,不需要获取对象的实现类对象,那如何获取类加载器?
1 2 3 ClassLoader classLoader = ProxyFactoryByMe.class.getClassLoader();ClassLoader classLoader = this .getClass().getClassLoader();
Class[] interfaces 获取目标对象实现的所有接口的class对象的数组
1 Class<?>[] interfaces = target.getClass().getInterfaces();
InvocatonHandler h 设置代理类中的抽象方法如何重写,这里使用了匿名内部类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 InvocationHandler h = new InvocationHandler () { @Override public Object invoke (Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { Object result = null ; try { System.out.println("日志 , 方法:" +method.getName()+"," +"参数:" + Arrays.toString(args)); result = method.invoke(target, args); System.out.println("日志 , 方法:" +method.getName()+"," +"结果::" + result); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("日志 , 方法:" +method.getName()+"," +"异常::" + e); } finally { System.out.println("结束" ); } return result; } };
上面的还是JDK动态代理
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Test public void testByProxyFactory () { ProxyFactoryByMe proxyFactoryByMe = new ProxyFactoryByMe (new CalculatorByMeImpl ()); CalculatorByMe proxy = (CalculatorByMe) proxyFactoryByMe.getProxy(); int result = proxy.div(2 , -1 ); }
动态代理的代码(工厂)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 package com.zzmr.spring.proxy;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;import java.lang.reflect.Method;import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;import java.util.Arrays;public class ProxyFactoryByMe { private Object target; public ProxyFactoryByMe (Object target) { this .target = target; } public Object getProxy () { ClassLoader classLoader = this .getClass().getClassLoader(); Class<?>[] interfaces = target.getClass().getInterfaces(); InvocationHandler h = new InvocationHandler () { @Override public Object invoke (Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { Object result = null ; try { System.out.println("日志 , 方法:" +method.getName()+"," +"参数:" + Arrays.toString(args)); result = method.invoke(target, args); System.out.println("日志 , 方法:" +method.getName()+"," +"结果::" + result); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("日志 , 方法:" +method.getName()+"," +"异常::" + e); } finally { System.out.println("结束" ); } return result; } }; return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, interfaces, h); } }
还有一个cglib动态代理,最终生成的代理类,汇集成目标类,并且和目标类在相同的包下
Java动态代理和cglib比较
生成代理类技术不同
java动态代理:jdk自带类ProxyGenerator生成class字节码
cglib:通过ASM框架生成class字节码文件
生成代理类的方式不同
java动态代理:代理类继承java.lang.reflect.Proxy,实现被代理类的接口
cglib:代理类继承被代理类,实现net.sf.cglib.proxy.Factory
生成类数量不同
java动态代理:生成一个proxy类
cglib:生成一个proxy,两个fastclass类
调用方式不同
java动态代理:代理类->InvocationHandler->反射调用被代理类方法
cglib:代理类->MethodInterceptor->调用索引类invoke->直接调用被代理类方法
性能比较
在 jdk6之前比使用 Java反射效率要高,在 jdk6、jdk7、jdk8 逐步对 JDK 动态代理优化之后,在调用次数较少的情况下,JDK 代理效率 高于 CGLIB 代理效率。只有当进行大量调用的时候,jdk6 和 jdk7 比 CGLIB 代理效率低一点,但是到 jdk8 的时候,jdk 代理效率高于 CGLIB 代理,总之,每一次 jdk 版本升级,JDK 代理效率 都得到提升,而 CGLIB 代理效率 确有点跟不上步伐。
手写动态代理以后是用的不多的,那为什么要写?因为AOP的实现原理就是这么来的,所以以后要使用动态代理,就直接使用AOP了,并不需要手写,手写只是为了更好得学习AOP
好了,马上进入正式的AOP
AOP概念 AOP是一种设计思想,也就是所谓的面向切面编程 ,它是面向对象编程的一种补充和完善,它以通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理方式实现在不修改源代码的情况下给程序动态统一添加额外功能的一种技术
相关术语 又是一堆枯燥无味的概念,这些东西不实现,是很难记住的,我发现我现在是惊醒越来越差了
害
横切关注点
什么是横切关注点?简单理解就是那些和核心业务无关的代码,比如前面的日志代码,那两行日志代码就是横切关注点
通知
每个横切关注点上要做的事情都需要写一个方法来实现,这样的方法就叫通知方法,也就是之前写的日志的代码,就相当于通知,只是分类有很多,比如之前写在核心代码前的,就是前置通知,这通知又分为好几种
前置通知:在被代理的目标方法前 执行
返回通知:在被代理的目标方法成功结束 后执行(寿终正寝)
异常通知:在被代理的目标方法异常结束 后执行(死于非命)
后置通知:在被代理的目标方法最终结束 后执行(盖棺定论)
环绕通知:使用try.catch/finally结构围绕整个被代理的目标方法,包括上面的四种通知对应的所有位置
切面
封装通知方法的类,这个之前好像没有
目标
被代理的目标对象
代理
向目标对象应用通知之后创建的代理对象
连接点
把方法排成一排,每个横切位置看成为x轴方向,把方法从上到下执行的顺序看成y轴,x轴和y轴的交叉点就是连接点
切入点
定位连接点的方式把连接点看作数据库中的记录,那么切入点就是查询记录的SQL语句,Spring的AOP技术可以通过切入点定位到特定的连接点
所以AOP的一个非常重要的操作就是抽,和套
作用
简化代码:把方法中固定位置的重复的代码抽取出来,让被抽取的方法更专注于自己的核心功能,提高内聚性
代码增强,把特定的功能封装到切面类中,看哪里有需要,就往上套,被套用了切面逻辑的方法就被切面给增强了
基于注解的AOP 三种实现方式
动态代理
cglib
Aspectj(本质上是静态代理)
注意事项:
交给IOC容器管理,这里是使用注解,所以只需要在普通类上面加上@Component注释
代理类的代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 package com.zzmr.spring.aop.annotation;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component @Aspect public class LoggerAspectByMe { @Before("execution(public int com.zzmr.spring.aop.annotation.CalculatorImpl.add(int,int))") public void beforeAdviceMethod () { System.out.println("LoggerAspect,Before" ); } }
这里如果直接使用IOC获取目标对象,是获取不到的
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Test public void testBefore () { ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ("aop-annotation.xml" ); CalculatorImpl calculator = ioc.getBean(CalculatorImpl.class); int result = calculator.add(1 , 1 ); }
这个时候会直接报错-NoSuchBeanDefinitionException
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Test public void testBefore () { ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ("aop-annotation.xml" ); Calculator calculator = ioc.getBean(Calculator.class); calculator.add(1 ,1 ); }
这个时候就不会报错了
问题也出现了,看上面的切入点表达式:
1 @Before("execution(public int com.zzmr.spring.aop.annotation.CalculatorImpl.add(int,int))")
这就相当于方法写死了,只能定位到add方法里面了
改进对切入点表达式进行改进
1 @Before("execution(* com.zzmr.spring.aop.annotation.CalculatorImpl.*(..))")
这样就能给指定类中的所有方法加上通知了
以此类推,在类的位置上写上星号,就代表当前包下所有的类
1 @Before("execution(* com.zzmr.spring.aop.annotation.*.*(..))")
此时还有问题,怎么在通知方法中获取连接点信息?就是获取被代理的目标方法的信息,这里需要在通知方法中添加JoinPoint参数
JoinPoint.getSignature()可以获取连接点对应方法的签名信息(内含方法名)
JoinPoint.getArgs()可以获取对应方法的参数列表
那如何获取方法的返回类型?有一个MethodSignature,可以通过signature获取
1 2 MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature) signature;System.out.println("方法的返回类型:" + methodSignature.getReturnType());
下面是代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @Before("execution(* com.zzmr.spring.aop.annotation.CalculatorImpl.*(..))") public void beforeAdviceMethod (JoinPoint joinPoint) { Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature(); Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs(); System.out.println("LoggerAspect,Before" ); System.out.println("LoggerAspect,方法名:" +signature.getName()+"," +"参数列表" + Arrays.toString(args)); }
测试:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 @Test public void testBefore () { ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ("aop-annotation.xml" ); Calculator calculator = ioc.getBean(Calculator.class); calculator.add(1 ,2 ); System.out.println("============" ); calculator.sub(1 ,1 ); System.out.println("============" ); calculator.mul(1 ,1 ); System.out.println("============" ); calculator.div(1 ,1 ); }
结果:
切入点表达式重用
很简单,只需要写一个方法,在方法的上面写上@Pointcut注解,里面写上要重用的切入点表达式即可
1 2 @Pointcut("execution(* com.zzmr.spring.aop.annotation.CalculatorImpl.*(..))") public void pointCut () {}
使用时:
1 2 3 4 @After("pointCut()") public void afterAdviceMethod () { System.out.println("后置通知" ); }
前置通知:@Before()
后置通知:@After()
返回通知:@AfterReturning()
1 2 3 4 5 @AfterReturning(value = "pointCut()", returning = "result") public void afterReturningAdviceMethod (JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result) { Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature(); System.out.println("返回通知,方法:" + signature.getName() + "," + "结果:" + result); }
异常通知:@AfterThrowing()
1 2 3 4 5 @AfterThrowing(value = "pointCut()",throwing = "ex") public void afterThrowingAdviceMethod (JoinPoint joinPoint,Throwable ex) { Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature(); System.out.println("异常通知,方法名:" +signature.getName()+", 异常:" +ex); }
此时比如还是1/0,看结果:
这里还要注意:
Spring版本5.3.x以前
Spring版本5.3.x以后
环绕通知
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 @Around("pointCut()") public Object aroundAdviceMethod (ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) { Object result = null ; try { System.out.println("环绕通知:前置通知" ); result = joinPoint.proceed(); System.out.println("环绕通知:返回通知" ); } catch (Throwable e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("环绕通知:异常通知" ); } finally { System.out.println("环绕通知:后置通知" ); } return result; }
但是以后用的话要么是四个普通的,要么就是一个环绕,不可能同时用两种
切面的优先级 上面写的是日志功能的切面,而以后还有事务功能的切面,验证功能的切面
每个切面都有一个优先级:@Order()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 package com.zzmr.spring.aop.annotation;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component @Aspect @Order public class ValidateAspectByMe { @Before("execution(* com.zzmr.spring.aop.annotation.CalculatorImpl.*(..))") public void beforeMethod () { System.out.println("ValidateAspect--->前置通知" ); } }
此时,ValidateAspectByMe就要比之前的切面优先级高了,可以先执行
基于XML的AOP 这个只是了解,以后用大部分时候使用基于注解的AOP
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd" > <context:component-scan base-package ="com.zzmr.spring.aop.xml" > </context:component-scan > <aop:config > <aop:pointcut id ="pointCut" expression ="execution(* com.zzmr.spring.aop.xml.CalculatorImpl.*(..))" /> <aop:aspect ref ="loggerAspectByMe" > <aop:before method ="beforeAdviceMethod" pointcut-ref ="pointCut" > </aop:before > <aop:after method ="afterAdviceMethod" pointcut-ref ="pointCut" > </aop:after > <aop:after-returning method ="afterReturningAdviceMethod" returning ="result" pointcut-ref ="pointCut" > </aop:after-returning > <aop:after-throwing method ="afterThrowingAdviceMethod" pointcut-ref ="pointCut" throwing ="ex" > </aop:after-throwing > <aop:around method ="aroundAdviceMethod" pointcut-ref ="pointCut" > </aop:around > </aop:aspect > </aop:config > </beans >
没啥难的,也没啥需要注意的哈哈哈哈
测试:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 package com.zzmr.spring.test;import com.zzmr.spring.aop.xml.Calculator;import org.junit.Test;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;public class AopXMLTest { @Test public void testXML () { ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ("aop-xml.xml" ); Calculator bean = ioc.getBean(Calculator.class); bean.add(1 ,1 ); } }
马上就是AOP的应用了
声明式事务 下面就到了给事务代码实现AOP了
但是在那之前,要先学习一下JdbcTemplate,这个是Spring封装的JDBC,但是这个只是了解一下,以后还是用MyBatis用的多
创建一个spring-jdbc.xml配置文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 <context:property-placeholder location ="classpath:jdbc.properties" /> <bean id ="dataSource" class ="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" > <property name ="driverClassName" value ="${jdbc.driver}" > </property > <property name ="url" value ="${jdbc.url}" > </property > <property name ="username" value ="${jdbc.username}" > </property > <property name ="password" value ="${jdbc.password}" > </property > </bean > <bean class ="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate" > <property name ="dataSource" ref ="dataSource" > </property > </bean >
这里有一个小的注意点,就是Spring有一个整合的junit,要引入依赖:但是之前的Junit的依赖还是不能丢掉的,还是要保留
1 2 3 4 5 6 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework</groupId > <artifactId > spring-test</artifactId > <version > 5.3.1</version > </dependency >
然后给测试类上添加上两个注解
//指定当前测试类在spring的测试环境中执行,此时就可以通过注入的方式直接获取IOC容器中的bean
//设置Spring测试环境的配置文件
大白话说着不清楚,还是直接看代码吧
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 package com.zzmr.spring.test;import org.junit.Test;import org.junit.runner.RunWith;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration("classpath:spring-jdbc.xml") public class JdbcTemplateTestTwo { @Autowired private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; @Test public void testInsert () { String sql = "insert into t_user values(null,?,?,?,?,?)" ; jdbcTemplate.update(sql,"jimmy" ,"010203" ,23 ,"男" ,"123456@163.com" ); } }
这里重点就是Spring的测试方法,可以直接使用两个注解来实现自动装配某个组件,比如这个JdbcTemplate,像之前的那个什么IOC容器也一样,就不用写一个测试方法就写一个ApplicationContext了
下面看查询的方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 @Test public void testGetUserById () { String sql = "select * from t_user where id = ?" ; User user = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper <>(User.class), 1 ); System.out.println(user); } @Test public void testGetAllUser () { String sql = "select * from t_user" ; List<User> userList = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper <>(User.class)); userList.forEach(System.out::println); } @Test public void testGetCount () { String sql = "select count(*) from t_user" ; Integer count = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, Integer.class); System.out.println(count); }
也非常简单
而声明式事务正是解决这一痛点而出现的
提高开发效率
消除了冗余代码
框架会综合考虑相关领域中在实际开发环境下有可能遇到的各种问题.进行了健壮性,性能等各个方面的优化
而且,重要的是声明式事务的代码都已经写好了,都是直接拿来用的,连通知都不用写
基于注解的声明式事务 一个配置,一个注解,即完成了声明式事务
在配置之前,首先看一下什么时候需要事务,或者说什么时候需要回滚?这里假设一个条件,比如当用户购买书时,如果书的库存不足,那就会出问题,这里可以使用无符号的数据类型来限定库存余额 ,当然也可以在java代码中实现,比如,如果余额不足,那就抛出异常即可,没有异常就造异常
tx-annotation.xml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd" > <context:component-scan base-package ="com.zzmr.spring" > </context:component-scan > <context:property-placeholder location ="classpath:jdbc.properties" /> <bean id ="dataSource" class ="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" > <property name ="driverClassName" value ="${jdbc.driver}" > </property > <property name ="url" value ="${jdbc.url}" > </property > <property name ="username" value ="${jdbc.username}" > </property > <property name ="password" value ="${jdbc.password}" > </property > </bean > <bean class ="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate" > <property name ="dataSource" ref ="dataSource" > </property > </bean > <bean id ="transactionManager" class ="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" > <property name ="dataSource" ref ="dataSource" > </property > </bean > <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager ="transactionManager" /> </beans >
这里写上我自己写的代码吧
BookControllerByMe.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 package com.zzmr.spring.controller;import com.zzmr.spring.service.BookServiceByMe;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;@Controller public class BookControllerByMe { @Autowired private BookServiceByMe bookServiceByMe; public void buyBookByMe (int userId,int bookId) { bookServiceByMe.buyBookByMe(userId,bookId); } }
BookServiceByMe.java
1 2 3 4 5 package com.zzmr.spring.service;public interface BookServiceByMe { void buyBookByMe (int userId, int bookId) ; }
BookServiceImplByMe.java但是由于在建表时指定了stock和balance是无符号的,所以当余额不足买书时数据库就会报错
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 package com.zzmr.spring.service.impl;import com.zzmr.spring.dao.BookDaoByMe;import com.zzmr.spring.service.BookServiceByMe;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;@Service public class BookServiceImplByMe implements BookServiceByMe { @Autowired private BookDaoByMe bookDaoByMe; @Override public void buyBookByMe (int userId, int bookId) { Integer bookPrice = bookDaoByMe.getPriceByIdByMe(bookId); bookDaoByMe.updateStock(bookId); bookDaoByMe.updateBalance(userId,bookPrice); } }
BookDaoByMe.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 package com.zzmr.spring.dao;public interface BookDaoByMe { Integer getPriceByIdByMe (Integer bookId) ; void updateStock (Integer bookId) ; void updateBalance (Integer userId,Integer price) ; }
BookDaoImplByMe.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 package com.zzmr.spring.dao.impl;import com.zzmr.spring.dao.BookDaoByMe;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;@Repository public class BookDaoImplByMe implements BookDaoByMe { @Autowired private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; @Override public Integer getPriceByIdByMe (Integer bookId) { String sql = "select price from t_book where book_id = ?" ; Integer price = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, Integer.class, bookId); return price; } @Override public void updateStock (Integer bookId) { String sql = "update t_book set stock = stock - 1 where book_id = ?" ; jdbcTemplate.update(sql,bookId); } @Override public void updateBalance (Integer userId,Integer price) { String sql = "update t_user1 set balance = balance - ? where user_id = ?" ; jdbcTemplate.update(sql,price,userId); } }
此时没有事务管理,用户余额为50,如果买第一本书,价格80,此时就会报错,但是由于MySql默认是一条Sql就会自动提交一次事务,所以就导致了库存是减少了,但是用户的余额并没有变
下面就是重头戏了,给service层添加上事务管理
出现异常就回滚
先看需要的配置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 <bean id ="transactionManager" class ="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" > <property name ="dataSource" ref ="dataSource" > </property > </bean > <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager ="transactionManager" />
配置”开启事务的注解驱动”后,就会发现左边出现了环绕通知的图标
给方法添加上事务管理
声明式事务的步骤:
在Spring的配置文件中配置事务管理器
开启事务的注解驱动
在需要被事务管理的方法上添加上@Transactional注解,该方法就会被事务管理
@Transactional注解标识的位置
标识在方法上
标识在类上,则类中所有的方法都会被事务管理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 @Override @Transactional public void buyBookByMe (int userId, int bookId) { Integer bookPrice = bookDaoByMe.getPriceByIdByMe(bookId); bookDaoByMe.updateStock(bookId); bookDaoByMe.updateBalance(userId,bookPrice); }
@Transactional的属性
只读
1 2 3 @Transactional( readOnly = true )
注意,如果设置了只读,这时如果进行修改,就会报SQLException:Connection is read-only. Queries leading to data modification are not allowed
超时
默认值是-1,意为一直等
1 2 3 @Transactional( timeout = 3 )
此时在service中,给这个程序休眠5s(在调用核心代码之前添加以下代码 )
1 2 3 4 5 try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
如果超时,则会报:TransactionTimedOutException: Transaction timed out: deadline was…
回滚策略
rollbackFor属性:需要设置一个Class类型的对象
rollbackForClassName属性:需要设置一个字符串类型的全类名
noRollbackFor属性:需要设置一个Class类型的对象
rollbackFor属性:需要设置一个字符串类型的全类名
不过一般情况下不需要设置回滚策略
看一种情况,比如在所有的更新库存更新余额执行完之后,执行一个sout(1/0),此时会抛出数学运算异常,但上面的更新是没问题的,由于还是抛出了异常,所以造成回滚
此时设置:
1 2 3 4 5 @Transactional( {noRollbackFor = ArithmeticException.class} // noRollbackForClassName = "java.lang.ArithmeticException" )
noRollbackFor是一个数组,但是如果只有一个数据的话,是不用写大括号的
就可以实现
事务的隔离级别
就那几个隔离级别,一般来说不需要设置,默认为”可重复读”-REPEATABLE READ-确保Transaction01可以多次从一个字段中读取到相同的值,即Transaction01执行期间禁止其他事务对这个字段进行更新串行化 ,确保Transaction01可以多次从一个表中读取到相同的行,在Transaction01执行期间,进制其他事务对这个表进行添加,更新,删除操作,可以避免任何并发问题,但性能十分低下只有特殊情况下才使用串行化,一般都是用默认的可重复读
各个隔离级别解决并发问题的能力:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @Transactional( //readOnly = true, //timeout = 3, //noRollbackFor = {ArithmeticException.class} //noRollbackForClassName = "java.lang.ArithmeticException", isolation = Isolation.DEFAULT )
事务的传播行为
来看代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 package com.zzmr.spring.service;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;public interface CheckoutService { void checkout (Integer userId, Integer[] bookIds) ; }
serviceImpl
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 package com.zzmr.spring.service.impl;import com.zzmr.spring.service.BookServiceByMe;import com.zzmr.spring.service.CheckoutService;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;@Service public class CheckoutServiceImpl implements CheckoutService { @Autowired private BookServiceByMe bookServiceByMe; @Override @Transactional public void checkout (Integer userId, Integer[] bookIds) { for (Integer bookId : bookIds) { bookServiceByMe.buyBookByMe(userId,bookId); } } }
测试类:
1 2 3 4 @Test public void testTwo () { bookControllerByMe.checkout(1 ,new Integer []{1 ,2 }); }
此时,就会发现,虽然钱能够买第一本书,但是由于买不起第二本书,所以事务回滚
此时在BookServiceImpl中
1 2 3 @Transactional( propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW )
此时就会发现,第一本能买成功,第二本不行
基于XML的声明式事务 此时先把BookServiceImpl和CheckoutServiceImpl中的@Transactional给注释掉,然后使用xml来实现以下,才发现之前甚至没有听这两节
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 <tx:advice id ="tx" transaction-manager ="transactionManager" > </tx:advice > <aop:config > <aop:advisor advice-ref ="tx" pointcut ="execution(* com.zzmr.spring.service.impl.*.*(..))" > </aop:advisor > </aop:config >
这个就是基于xml的声明式事务的配置信息
还有jar包,不然运行不了
1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework</groupId > <artifactId > spring-aspects</artifactId > <version > 5.3.1</version > </dependency >
SpringMVC开始
SpringMVC 2022年11月6日 20点25分快要开始做项目了,有点慌,跟他们学的东西不太一样,咱又没人家学的精,只能用人家的方法来写了
在这里再说一下,MyBatis是持久层框架,而Spring可以利用IOC和AOP来整合框架
三个概念:
你还记得吗,之前有一个什么请求,都要写一个对应的Servlet,而现在不需要了,现在DispatcherServlet就是一个整体的Servlet,不需要自己创建Servlet了
好久没写了,这段时间都在做项目/打游戏哈哈哈 2022年11月25日 15点13分
基本配置 配置web.xml 之前的web.xml要配置好多好多Servlet,而现在只需要配置一个-DispatcherServelt
url-pattern中 /表示匹配浏览器向服务器发送的所有请求(不包括jsp) /表示匹配浏览器向服务器发送的所有请求(包括jsp) ? 因为DispatcherServlet处理不了jsp的请求,jsp会被tomcat默认的配置-JspServlet来处理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <web-app xmlns ="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd" version ="4.0" > <servlet > <servlet-name > SpringMVC</servlet-name > <servlet-class > org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class > </servlet > <servlet-mapping > <servlet-name > SpringMVC</servlet-name > <url-pattern > /</url-pattern > </servlet-mapping > </web-app >
创建请求控制器 前端控制器处理了所有浏览器发送的请求,但是具体的请求有不同的处理过程,就需要创建处理具体请求的类-请求控制器,这个类不需要继承什么,只需要加上@Controller注解,那这个普通的类就变成了请求控制器,不过要想实现这个操作,需要在SpringMVC的配置文件中扫描对应的包才行
请求控制器中每一个处理请求的方法称为控制器方法
1 2 3 4 @Controller public class HelloController {}
创建SpringMVC的配置文件 SpringMVC的配置文件是在SpringMVC初始化时完成加载的实际上配置文件还是要放在resources下,然后在web.xml中引入即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd" > <context:component-scan base-package ="com.zzmr.controller" /> <bean id ="viewResolver" class ="org.thymeleaf.spring5.view.ThymeleafViewResolver" > <property name ="order" value ="1" /> <property name ="characterEncoding" value ="UTF-8" /> <property name ="templateEngine" > <bean class ="org.thymeleaf.spring5.SpringTemplateEngine" > <property name ="templateResolver" > <bean class ="org.thymeleaf.spring5.templateresolver.SpringResourceTemplateResolver" > <property name ="prefix" value ="/WEB-INF/templates/" /> <property name ="suffix" value =".html" /> <property name ="templateMode" value ="HTML5" /> <property name ="characterEncoding" value ="UTF-8" /> </bean > </property > </bean > </property > </bean > </beans >
配置了什么视图前缀 ,视图后缀 之后,就可以直接通过逻辑视图(视图的名字)来访问了
创建控制器方法 下文中的斜线/ 表示的是localhost:8080/上下文路径/
1 2 3 4 5 6 @RequestMapping("/") public String portal () { return "index" ; }
当浏览器发送一个请求,如果请求路径和@RequestMapping的括号里面的路径是一样的话,这个请求就会被该控制器方法处理 在return之后,就会被视图解析器解析,然后在逻辑视图前面加上视图前缀,在逻辑视图后面加上视图后缀:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 <bean class ="org.thymeleaf.spring5.templateresolver.SpringResourceTemplateResolver" > <property name ="prefix" value ="/WEB-INF/templates/" /> <property name ="suffix" value =".html" /> <property name ="templateMode" value ="HTML5" /> <property name ="characterEncoding" value ="UTF-8" /> </bean >
测试 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" xmlns:th ="http://www.thymeleaf.org" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > 首页</title > </head > <body > <h1 > index.html</h1 > <a th:href ="@{/hello}" > 测试SpringMVC</a > <br > </body > </html >
这里使用的是thymeleaf解析的路径,也就是下面的th:href=”@{/hello}”
到这里,其实还有一些扩展的东西
将SpringMVC配置文件放到resource目录下的操作:初始化参数,指定param-name和param-value就行了,param-value就是配置文件的文件名
而load-on-startup标签是将DispatcherServlet的初始化时间提前到服务器启动时
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 <servlet > <servlet-name > SpringMVC</servlet-name > <servlet-class > org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class > <init-param > <param-name > contextConfigLocation</param-name > <param-value > classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value > </init-param > <load-on-startup > 1</load-on-startup > </servlet >
@RequestMapping注解 开始深入了
首先做的还是简单的配置
复制pom.xml中的一些依赖,从打包方式开始,一直复制到最后
然后配置web.xml,就是配置servlet(DispatcherServlet)
然后配置springmvc配置文件(直接复制之前的,因为基本没什么区别)
配置完,就开始写controller了
可以单独写一个访问首页的控制器-PortalController.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 package com.zzmr.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;@Controller public class PortalController { @RequestMapping("/") public String portal () { return "index" ; } }
@RequestMapping注解的功能 @RequestMapping注解的作用就是将请求和处理请求的控制器方法关联起来,建立映射关系
@RequestMapping注解可标识的位置
标识在方法上,设置映射请求路径的具体信息
标识到类上,设置映射请求路径的初始信息要先匹配类上的路径,再匹配到方法上的路径,才能处理请求 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 package com.zzmr.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;@Controller @RequestMapping("/test") public class TestRequestMappingController { @RequestMapping("/hello") public String hello () { return "success" ; } }
此时类上的是/test,而方法上的是/hello
1 <a th:href ="@{/hello}" > 测试@RequestMapping注解所标识的位置</a >
就访问不到,要写成这样:
1 <a th:href ="@{/test/hello}" > 测试@RequestMapping注解所标识的位置</a >
也就是类上的路径加上方法的路径才是一个完整的路径
这个是非常有用的,举个例子,老师和学生同时有一个查询的方法,请求路径都是/list,此时SpringMVC就不能分辨到底是学生的/list还是老师的/list,就会报错,在类上添加注解,可以解决这个问题,比如在学生类上添加/student,而请求查询所有学生信息就用的是/student/list,查询老师就是/teacher/list,这样就不会冲突了
@RequestMapping的value属性 这个value属性,其实就是路径,可以设置多个:
1 2 3 4 @RequestMapping({"/hello", "/abc"}) public String hello () { return "success" ; }
设置多个的效果:该控制器方法可以处理多个请求:
1 2 <a th:href ="@{/hello}" > 测试@RequestMapping注解所标识的位置</a > <a th:href ="@{/abc}" > 测试@RequestMapping注解所标识的位置</a >
此时两个都能访问到
之前的servlet也是可以实现的,只需要多设置几个url-pattern
明天见
@RequestMapping的method属性 通过请求的请求方式匹配请求,浏览器所发送请求的请求方式匹配method属性中的任意一个,即可响应请求
这里的method,之前只学过POST和GET,什么时候是POST,什么时候是GET?POST请求只在form表单提交时改为post出现,其余皆为GET
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @RequestMapping( value = {"/hello", "/abc"}, method = {RequestMethod.POST} ) public String hello () { return "success" ; }
此时就只能处理post请求了
1 2 3 4 <a th:href ="@{/abc}" > 测试@RequestMapping的value属性</a > <br > <form th:action ="@{/hello}" method ="post" > <input type ="submit" value ="测试@RequestMapping的method属性" > </form >
这两个,就只能下面的form表单能请求成功,因为是post请求,上面的是get请求
改成:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @RequestMapping( value = {"/hello", "/abc"}, method = {RequestMethod.POST,RequestMethod.GET} ) public String hello () { return "success" ; }
此时既能处理get,也能处理post
405错误:若浏览器所发送的请求的请求路径和@RequestMapping注解value属性匹配,但是请求方式不匹配,此时页面报错,405 - Request method ‘xxx’ not supported
@RequestMapping的param属性
在@RequestMapping的基础上,结合请求方式的一些派生注解:
@RequestMapping注解的params属性
作用:通过请求的请求参数匹配请求,即浏览器发送的请求的请求参数必须满足params属性
“param”: 表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中必须携带param参数
“!param”: 表示当前所匹配请求参数必须不能携带param参数
“param=value”: 表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数中必须携带param参数且值必须为value
“param!=value”: 表示当前所匹配请求的请求参数可以不携带param,如果携带,必须不能等于value
下面的params条件就是,必须有username,必须不能有password,必须有age,且等于20,gender可以不携带,但如果携带不能为男
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @RequestMapping( value = {"/hello", "/abc"}, method = {RequestMethod.POST,RequestMethod.GET}, params = {"username","!password","age=20","gender!=男"} ) public String hello () { return "success" ; }
如果遇到params属性不匹配的情况,就会报这个错误:
那如何设置请求参数呢,有两种方式:
直接?拼接1 <a th:href ="@{/hello?username=admin}" > 测试params属性</a >
小括号的形式1 <a th:href ="@{/hello(username='admin')}" > 测试params属性</a >
有什么区别吗?没有,只是第一种写法,会报红,但实际运行时没问题
但是param用的并不多,还是value和method用的比较多
随便写点吧,反正是了解
这四种和上面的params类似,但又有些区别
若当前请求满足@RequestMapping注解的value和method属性,但是不满足headers属性,此时页面显示404错误,即资源未找到
SpringMVC支持ant风格的路径 说白了就是用特殊符号来表示路径片段
?:表示任意的单个字符
*:表示任意的0个或多个字符
**:表示任意层数的任意目录
示例1:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @RequestMapping("/a?c/test/ant") public String testAnt () { return "success" ; }
此时就可以匹配a(任意字符)c的请求了,但是某些特殊字符是不行的,比如?
1 2 3 <a th:href ="@{/abc/test/ant}" > 测试Ant</a > <a th:href ="@{/acc/test/ant}" > 测试Ant</a > <a th:href ="@{/adc/test/ant}" > 测试Ant</a >
示例2:
1 2 3 4 @RequestMapping("/a*c/test/ant") public String testAnt () { return "success" ; }
此时可以匹配任意个数的任意字符,但是也不能有特殊字符:?,/
示例3:
1 2 3 4 @RequestMapping("/**/test/ant") public String testAnt () { return "success" ; }
此时可以表示任意层数的任意目录,但是要注意写法:**只能写在双斜线中,前后不能有任何的字符
SpringMVC支持路径中的占位符(重点) 原始方式: /deleteUser?id=1
SpringMVC路径中的占位符常用于RESTful更各种,当请求路径种将某些数据通过路径的方式传输到服务器中,就可以在相应的@RequestMapping注解的value属性中通过占位符{xxx}表示传输的数据,在通过@PathVariable注解,将占位符所表示的数据赋值给控制器方法的形参
说白了就是将发送的请求参数也作为路径的一部分
主要就是要用{}和@PathVariable(“”),
1 2 3 4 5 6 @RequestMapping("/test/rest/{username}/{id}") public String testRest (@PathVariable("id") Integer id, @PathVariable("username") String username) { System.out.println("id: " + id); System.out.println("username: " + username); return "success" ; }
此时:
1 <a th:href ="@{/test/rest/admin/1}" > 测试@ReqeustMapping注解的value属性中的占位符</a >
后端就可以获取到admin和1了
SpringMVC获取请求参数
通过ServletAPI获取,也就是老式的获取方式,主要就是要注意request是从哪里来的,是前端控制器检测方法用的是什么,就会给什么1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @RequestMapping("/param/servletAPI") public String getParamByServletAPI (HttpServletRequest request) { String username = request.getParameter("username" ); String password = request.getParameter("password" ); System.out.println("username: " + username); System.out.println("password: " + password); return "success" ; }
1 2 3 4 5 <form th:action ="@{/param/servletAPI}" method ="post" > 用户名: <input type ="text" name ="username" > <br > 密码: <input type ="password" name ="password" > <br > <input type ="submit" value ="登录" > </form >
通过控制器方法的形参获取1 2 3 4 5 6 @RequestMapping("/param") public String getParam (String username,String password) { System.out.println("username: " + username); System.out.println("password: " + password); return "success" ; }
1 2 3 4 5 <form th:action ="@{/param}" method ="post" > 用户名: <input type ="text" name ="username" > <br > 密码: <input type ="password" name ="password" > <br > <input type ="submit" value ="登录" > </form >
但是如果请求参数和形参名不一致呢,也就是自己设置的不一致,此时可以使用@RquestParam注解
1 2 3 4 5 6 @RequestMapping("/param") public String getParam (@RequestParam("userName") String username, String password) { System.out.println("username: " + username); System.out.println("password: " + password); return "success" ; }
但是我感觉多此一举 ,相当于多一个映射,用于请求参数和形参不一致的情况
还有就是@RequestParam注解的其他属性值
required,默认为true,表示必须传这个参数,如果不传,报400
defaultValue,当设置了defaultValue时,无论required是true还是false,当没传参数时,就是用默认值,传了,那就使用传的参数1 2 3 4 5 6 @RequestMapping("/param") public String getParam (@RequestParam(value = "userName",required = false,defaultValue = "hello") String username, String password) { System.out.println("username: " + username); System.out.println("password: " + password); return "success" ; }
@RequestHeader: 将请求头信息和控制器方法的形参绑定
@CookieValue: 将Cookie数据和控制器方法的形参绑定
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 @RequestMapping("/param") public String getParam ( @RequestParam(value = "userName", required = false, defaultValue = "hello") String username, String password, @RequestHeader("referer") String referer, @CookieValue("JSESSIONID") String jsessionId ) { System.out.println("username: " + username); System.out.println("password: " + password); System.out.println("referer:" + referer); System.out.println("jsessionId:" + jsessionId); return "success" ; }
当然获取cookie的前提是要有,所以在上面的/param/servletAPI中添加了:
1 HttpSession session = request.getSession();
此时先访问/param/servletAPI,然后再访问/param,就可以获取到jsessionId的cookie了
通过pojo获取请求参数 这种以后用的也是很多
1 2 3 4 5 @RequestMapping("/param/pojo") public String getParamByPojo (User user) { System.out.println(user); return "success" ; }
只需要在控制器方法的形参位置设置实体类类型的形参,要保证实体类中的属性的属性名和请求参数的名字一致,就可以实体类类型的形参获取请求参数这种也是用的最多的一种方式
解决获取请求参数的乱码问题 解决获取请求参数的乱码问题,可以使用SpringMVC提供的编码过滤器CharacterEncodingFilter,但是必须在web.xml中进行注册
把这个放到web.xml中就可以了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 <filter > <filter-name > CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name > <filter-class > org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class > <init-param > <param-name > encoding</param-name > <param-value > UTF-8</param-value > </init-param > <init-param > <param-name > forceEncoding</param-name > <param-value > true</param-value > </init-param > </filter > <filter-mapping > <filter-name > CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name > <url-pattern > /*</url-pattern > </filter-mapping >
还有一个要注意的地方
SpringmVC中处理编码的过滤器一定要配置在其他过滤器之前,否则无效
域对象共享数据 使用ServletAPI向request域对象共享数据 这还是老式的方式setAttribute()
使用ModelAndView向request域对象共享数据
不管使用的是哪种方式,到最后都会被转换为ModelAndView的形式共享数据,这也是为什么推荐使用这个的原因
具体步骤:
创建ModelAndView对象
共享数据:addObject()
设置视图:setViewName()注意,如果使用ModelAndView,就必须将ModelAndView对象返回
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 @RequestMapping("/test/mav") public ModelAndView testModelAndView () { ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView (); mav.addObject("testRequestScope" ,"hello,ModelAndView" ); mav.setViewName("success" ); return mav; }
那如何获取数据呢?
1 2 <p th:text ="${testRequestScope}" > </p >
使用Model向请求域中共享数据 这可能是最常用的方式了,因为相较于ModelAndView,这个明显简单一些
对象不用自己创建,直接写在形参位置即可
视图直接返回,不需要setView对象1 2 3 4 5 @RequestMapping("/test/model") public String testModel (Model model) { model.addAttribute("testRequestScope" ,"hello,Model" ); return "success" ; }
使用ModelMap向请求域中共享数据 这种也是很简单,几乎一模一样
1 2 3 4 5 @RequestMapping("/test/modelMap") public String testModelMap (ModelMap modelMap) { modelMap.addAttribute("testRequestScope" ,"hello,ModelMap" ); return "success" ; }
使用map向请求域中共享数据 区别仅在于形参的对象不同
1 2 3 4 5 @RequestMapping("/test/map") public String testMap (Map<String,Object> map) { map.put("testRequestScope" ,"hello,map" ); return "success" ; }
Model和ModelMap和map的关系 无论是使用Model,ModelMap,Map,底层都是同一个类:
向session域和application域中共享数据 建议还是使用老式的共享方式:setAttribute
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @RequestMapping("/test/session") public String testSession (HttpSession session) { session.setAttribute("testSessionScope" ,"hello,Session" ); return "success" ; } @RequestMapping("/test/application") public String testApplication (HttpSession session) { ServletContext servletContext = session.getServletContext(); servletContext.setAttribute("testApplicationScope" ,"hello,application" ); return "success" ; }
两个一块写了,主要就是记好如何往域中共享数据
而获取域中的数据:
1 2 3 <p th:text ="${session.testSessionScope}" > </p > <p th:text ="${application.testApplicationScope}" > </p >
SpringMVC的视图 SpringMVC中的视图是View接口,视图的作用是渲染数据,将模型Model中的数据展示给用户
ThymeleafView 当控制器方法中所设置的视图名称没有任何前缀时,此时的视图名称会被SpringMVC配置文件中所配置的视图解析器解析,视图名称拼接视图前缀和视图后缀所得到的最终路径,会通过转发的方式实现跳转
InternalResourceView 就是在视图前加上”forward:”
1 2 3 4 5 @RequestMapping("/test/view/forward") public String testInternalResourceView () { return "forward:/test/model" ; }
但是这个用的不多的,因为原来实现的就是转发,这个也是转发以后用的最多的还是Thymeleaf
重定向视图RedirectView 1 2 3 4 @RequestMapping("/test/view/redirect") public String testRedirectView () { return "redirect:/test/model" ; }
总结来说,使用转发视图时,使用Thymeleaf视图,使用重定向时,使用重定向视图,而访问页面失败时,就使用转发,访问成功就使用重定向
视图控制器view-controller 当控制器方法中,仅仅用来实现页面跳转,即只需要设置视图名称时,可以将处理器方法使用view-controller标签进行表示
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 <mvc:annotation-driven /> <mvc:view-controller path ="/" view-name ="index" />
通过标签实现页面跳转
RESTful RESTful简介
其实我又开始迷茫了
创建新的工程
我也不知道到底有什么用,反正就是看吧,看明白就好
RESTful模拟CRUD 要注意,form表单只有两种提交方式,get和post,是没有put和delete的,要想实现这两种方式,需要以下步骤:
设置过滤器(要注意一定要设置在编码过滤器的后面)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 <filter > <filter-name > HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name > <filter-class > org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-class > </filter > <filter-mapping > <filter-name > HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name > <url-pattern > /*</url-pattern > </filter-mapping >
设置name为_method的input标签,并保证form表单是post请求方式1 2 3 4 <form th:action ="@{/user}" method ="post" > <input type ="hidden" name ="_method" value ="put" > <input type ="submit" value ="修改用户信息" > </form >
name必须为_method,value为要设置的请求方式
那代码都在这了,因为没啥难的,所以就一块放了
这里使用了派生注解
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 package com.zzmr.controller;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;@Controller public class TestRestController { @GetMapping("/user") public String getAllUser () { System.out.println("查询所有的用户信息--->/user-->get" ); return "success" ; } @GetMapping("/user/{id}") public String getUserById (@PathVariable("id") Integer id) { System.out.println("根据id查询用户信息--->/user/" + id + "-->get" ); return "success" ; } @PostMapping("/user") public String insertUser () { System.out.println("添加用户信息--->/user-->post" ); return "success" ; } @PutMapping("/user") public String updateUser () { System.out.println("修改用户信息--->/user-->put" ); return "success" ; } @DeleteMapping("/user/{id}") public String deleteUser (@PathVariable("id") Integer id) { System.out.println("删除用户信息--->/user/" + id + "-->delete" ); return "success" ; } }
然后就是页面
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" xmlns:th ="http://www.thymeleaf.org" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > 首页</title > </head > <body > <h1 > index.html</h1 > <a th:href ="@{/user}" > 查询所有的用户信息</a > <br > <a th:href ="@{/user/2}" > 根据id查询用户</a > <br > <form th:action ="@{/user}" method ="post" > <input type ="submit" value ="添加用户信息" > </form > <form th:action ="@{/user}" method ="post" > <input type ="hidden" name ="_method" value ="put" > <input type ="submit" value ="修改用户信息" > </form > <form th:action ="@{/user/1}" method ="post" > <input type ="hidden" name ="_method" value ="delete" > <input type ="submit" value ="删除用户信息" > </form > </body > </html >
RESTful案例 这次所谓的测试并没有链接数据库,还是只是模拟一下
真的是,用了新键盘两天,就感觉原来的键盘手感怪怪的
这个案例好像也学不到什么,但是可以学一下,如何展示集合中的数据 th:each=”employee : ${域中集合的name}”,那么employee就表示集合中的每一项
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 <table > <tr > <th colspan ="5" > employee list</th > </tr > <tr > <th > id</th > <th > lastName</th > <th > email</th > <th > gender</th > <th > options</th > </tr > <tr th:each ="employee : ${allEmployee}" > <td th:text ="${employee.id}" > </td > <td th:text ="${employee.lastName}" > </td > <td th:text ="${employee.email}" > </td > <td th:text ="${employee.gender}" > </td > <td > <a th:href ="" > delete</a > <a th:href ="" > update</a > </td > </tr > </table >
静态资源的访问
解决办法
1 2 <mvc:default-servlet-handler />
但是想用这个,还需要:
1 <mvc:annotation-driven />
此时就实现了:请求先让DispatcherServlet处理,如果处理不了,比如静态资源,再转给默认的servlet处理(tomcat自带的)
还有一个要注意的点,之前写的默认跳转首页的那个,其实还可以用到一些其他地方,比如要跳转到添加页面,此时是不需要controller处理的,就让它直接跳过去,就可以直接在springmvc.xml中配置上
1 <mvc:view-controller path ="/to/add" view-name ="employee_add" />
还有要注意的地方
1 <a th:href ="@{'/employee/'+${employee.id}}" > update</a >
单引号括起来,然后用加号拼接
然后,写了一堆vue,我已经啥都不会了哈哈哈哈
然后把代码放着吧
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 package com.zzmr.controller;import com.zzmr.dao.EmployeeDao;import com.zzmr.pojo.Employee;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.ui.Model;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;import java.util.Collection;@Controller public class EmployeeController { @Autowired private EmployeeDao employeeDao; @RequestMapping(value = "/employee", method = RequestMethod.GET) public String getAllEmployee (Model model) { Collection<Employee> allEmployee = employeeDao.getAll(); model.addAttribute("allEmployee" , allEmployee); return "employee_list" ; } @RequestMapping(value = "/employee", method = RequestMethod.POST) public String addEmployee (Employee employee) { employeeDao.save(employee); return "redirect:/employee" ; } @RequestMapping(value = "/employee/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET) public String toUpdateEmployee (@PathVariable("id") Integer id, Model model) { Employee employee = employeeDao.get(id); model.addAttribute("employee" , employee); return "employee_update" ; } @RequestMapping(value = "/employee",method = RequestMethod.PUT) public String updateEmployee (Employee employee) { employeeDao.save(employee); return "redirect:/employee" ; } @RequestMapping(value = "/employee/{id}",method = RequestMethod.DELETE) public String deleteEmployee (@PathVariable("id") Integer id) { employeeDao.delete(id); return "redirect:/employee" ; } }
SpringMVC处理ajax请求 之前学过吗?忘了,翻翻web的笔记看看,还真是学过,笑死,忘的一干二净
好久没见了
axios 这个又是什么?这个没啥印象好像
手好干啊,摸这个新键盘有一种让人起鸡皮疙瘩的感觉
我甚至都不知道在写什么
@RequestBody注解的使用=>将请求体中的内容和控制器方法的形参进行绑定将json格式的请求参数转换为java对象
导入jackson的依赖
在SpringMVC的配置文件中设置开启mvc的注解驱动:mvc:annotation-driven
在处理请求的控制器方法的形参位置直接设置json格式的请求参数要转化的java类型的形参,使用@RequestBody注解标识即可
@ResponseBody,将所标识的控制器方法的返回值作为响应报文的响应体响应到浏览器
导入jackson的依赖
在SpringMVC的配置文件中设置开启mvc的注解驱动:mvc:annotation-driven
将需要转化为json字符串的java对象直接作为控制器方法的返回值,使用@ResponseBody注解标识控制器方法,就可以将java对象直接转化为json字符串,并响应到浏览器
1 2 3 4 5 6 @RequestMapping("/test/ResponseBody/json") @ResponseBody public User testResponseBody () { User user = new User (1001 , "admin" , "123456" , 20 , "男" ); return user; }
总结来说,就听懂一点:服务器想给浏览器发送一个Java类时,可以使用@ResponseBody注解,这个注解可以将Java对象直接转化为json字符串返回到浏览器,不需要多余的操作,非常方便
常用的Java对象转化为json的结果
map集合:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @RequestMapping("/test/ResponseBody/json") @ResponseBody public Map<String,Object> testResponseBody () { User user1 = new User (1001 , "admin1" , "123456" , 20 , "男" ); User user2 = new User (1002 , "admin2" , "123456" , 20 , "男" ); User user3 = new User (1003 , "admin3" , "123456" , 20 , "男" ); Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap <>(); map.put("1001" ,user1); map.put("1002" ,user2); map.put("1003" ,user3); return map; }
list集合:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 @RequestMapping("/test/ResponseBody/json") @ResponseBody public List<User> testResponseBody () { User user1 = new User (1001 , "admin1" , "123456" , 20 , "男" ); User user2 = new User (1002 , "admin2" , "123456" , 20 , "男" ); User user3 = new User (1003 , "admin3" , "123456" , 20 , "男" ); List<User> users = Arrays.asList(user1, user2, user3); return users; }
其实这些东西也没啥难的吧
还有一个注解也挺有用的@RestController注解
文件上传和下载 文件上传和下载
文件下载 ResponseEntity用于控制器方法的返回值类型,该控制器方法的返回值就是响应到浏览器的响应报文,使用ResponseEntity实现下载文件的功能
要注意getRealPath()方法,这个方法如果括号里不写字符串,则返回的是整个项目在服务器中的位置,如果加上了字符串,则会将字符串拼接到位置的后面
下载的代码,基本相似,以后用到直接复制就行
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 @RequestMapping("/test/down") public ResponseEntity<byte []> testResponseEntity(HttpSession session) throws IOException { ServletContext servletContext = session.getServletContext(); String realPath = servletContext.getRealPath("img" ); realPath = realPath + File.separator + "11.png" ; InputStream is = new FileInputStream (realPath); byte [] bytes = new byte [is.available()]; is.read(bytes); MultiValueMap<String, String> headers = new HttpHeaders (); headers.add("Content-Disposition" , "attachment;filename=11.png" ); HttpStatus statusCode = HttpStatus.OK; ResponseEntity<byte []> responseEntity = new ResponseEntity <>(bytes, headers, statusCode); is.close(); return responseEntity; }
文件上传 文件上传的条件:
form表单的请求方式必须为post
form表单必须设置属性enctype=”multipart/form-data”
先添加依赖:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 <dependency > <groupId > commons-fileupload</groupId > <artifactId > commons-fileupload</artifactId > <version > 1.3.1</version > </dependency > </dependencies >
控制器方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 @RequestMapping("/test/up") public String testUp (MultipartFile photo, HttpSession session) throws IOException { String fileName = photo.getOriginalFilename(); ServletContext servletContext = session.getServletContext(); String photoPath = servletContext.getRealPath("photo" ); File file = new File (photoPath); if (!file.exists()) { file.mkdir(); } String finalPath = photoPath + File.separator + fileName; photo.transferTo(new File (finalPath)); return "success" ; }
注意form表单
1 2 3 4 <form th:action ="@{/test/up}" method ="post" enctype ="multipart/form-data" > 头像<input type ="file" name ="photo" > <br > <input type ="submit" value ="上传" > </form >
以及配置文件中的bean
1 2 <bean id ="multipartResolver" class ="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver" > </bean >
id一定要为multipartResolver,为commonMultipartResolver就会报错,为其他的同样会报错
解决文件上传重名问题 1 2 3 4 5 String fileName = photo.getOriginalFilename();String hz = fileName.substring(fileName.lastIndexOf("." ));String uuid = UUID.randomUUID().toString();fileName = uuid + hz;
思路就是使用uuid,先用fileName.lastIndexOf()方法获取原始文件名最后的点的索引,然后使用substring()方法来截断,获取到后缀,再生成一个uuid,最后拼接
文件上传和下载也看完了,也没啥东西,主要就是思路
后面就是拦截器了?
看到这时候,又开始迷茫了,不做项目是进步不了的
拦截器 了解
配置拦截器 就了解一下如何配置拦截器吧
1 2 3 <mvc:interceptors > <bean class ="com.zzmr.interceptor.FirstInterceptor" > </bean > </mvc:interceptors >
这样就可以配置FirstInterceptor这个类为一个拦截器
其他的配置方式:ref,引用其他的bean
1 2 3 4 5 <bean id ="firstInterceptor" class ="com.zzmr.interceptor.FirstInterceptor" > </bean > <mvc:interceptors > <ref bean ="firstInterceptor" /> </mvc:interceptors >
还可以使用注解加扫描的形式
第三种配置方式,更精确,因为上面两种都是默认对所有的请求进行拦截,而下面这种可以更加的精确,也可以进行排除http://localhost:8080/SpringMVC/first,只能拦截一层目录,如果有多层则不进行拦截,/\*\*就表示所有目录
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 <mvc:interceptors > <mvc:interceptor > <mvc:mapping path ="/**" /> <mvc:exclude-mapping path ="/abc" /> <ref bean ="firstInterceptor" /> </mvc:interceptor > </mvc:interceptors >
拦截器中的方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 @Override public boolean preHandle (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { System.out.println("FirstInterceptor-->preHandle" ); return true ; } @Override public void postHandle (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception { System.out.println("FirstInterceptor-->postHandle" ); } @Override public void afterCompletion (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception { System.out.println("FirstInterceptor-->afterCompletion" ); }
拦截器的执行顺序 拦截器方法的执行:
preHandle() 在控制器方法执行之前 返回值表示对控制器方法的拦截(false)或放行(true)
postHandle() 在控制器方法执行之后
afterCompletion() 在控制器方法执行之后,且渲染视图完毕之后执行
多个拦截器的执行顺序 配置文件中的配置的顺序有关
preHandle()返回false的情况:
若拦截其中某个拦截器的preHandle()返回了false和它之前的拦截器的preHandle()都会执行
所有的拦截器的post()都不执行
拦截器的preHandle()返回false之前的拦截器的afterCompletion会执行
害,其实也没什么意义,就看看而已
异常处理 这块看之前的笔记吧,懒得写了
基于注解配置SpringMVC 这个好好看看吧
在Servlet3.0环境中,容器会在类路径中查找实现javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer接口的类,如果找到的话就用它来配置Servlet容器
创建初始化类,代替web.xml
在Servlet3.0环境中,容器会在类路径中查找实现javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer接口的类,如果找到的话就用它来配置Servlet容器
上代码吧注释都写好了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 package com.zzmr.config;import org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter;import org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilter;import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer;import javax.servlet.Filter;public class WebInit extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer { @Override protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() { return new Class []{SpringConfig.class}; } @Override protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() { return new Class []{WebConfig.class}; } @Override protected String[] getServletMappings() { return new String []{"/" }; } @Override protected Filter[] getServletFilters() { CharacterEncodingFilter characterEncodingFilter = new CharacterEncodingFilter (); characterEncodingFilter.setEncoding("UTF-8" ); characterEncodingFilter.setForceEncoding(true ); HiddenHttpMethodFilter hiddenHttpMethodFilter = new HiddenHttpMethodFilter (); return new Filter []{characterEncodingFilter, hiddenHttpMethodFilter}; } }
创建WebConfig来代替SpringMVC配置文件 还是挺多的,不过那个视图解析器可以直接复制,都是类似的内容
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 package com.zzmr.config;import com.zzmr.interceptor.FirstInterceptor;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader;import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;import org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver;import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver;import org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver;import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.*;import org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleMappingExceptionResolver;import org.thymeleaf.spring5.SpringTemplateEngine;import org.thymeleaf.spring5.view.ThymeleafViewResolver;import org.thymeleaf.templatemode.TemplateMode;import org.thymeleaf.templateresolver.ITemplateResolver;import org.thymeleaf.templateresolver.ServletContextTemplateResolver;import java.util.List;import java.util.Properties;@Configuration @ComponentScan("com.zzmr.controller") @EnableWebMvc public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer { @Override public void configureDefaultServletHandling (DefaultServletHandlerConfigurer configurer) { configurer.enable(); } @Override public void addViewControllers (ViewControllerRegistry registry) { registry.addViewController("/" ).setViewName("index" ); } @Bean public CommonsMultipartResolver multipartResolver () { return new CommonsMultipartResolver (); } @Override public void addInterceptors (InterceptorRegistry registry) { FirstInterceptor firstInterceptor = new FirstInterceptor (); registry.addInterceptor(firstInterceptor).addPathPatterns("/**" ); } @Override public void configureHandlerExceptionResolvers (List<HandlerExceptionResolver> resolvers) { SimpleMappingExceptionResolver simpleMappingExceptionResolver = new SimpleMappingExceptionResolver (); Properties properties = new Properties (); properties.setProperty("java.lang.ArithmeticException" , "error" ); simpleMappingExceptionResolver.setExceptionMappings(properties); simpleMappingExceptionResolver.setExceptionAttribute("ex" ); resolvers.add(simpleMappingExceptionResolver); } @Bean public ITemplateResolver templateResolver () { WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext = ContextLoader.getCurrentWebApplicationContext(); ServletContextTemplateResolver templateResolver = new ServletContextTemplateResolver (webApplicationContext.getServletContext()); templateResolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/templates/" ); templateResolver.setSuffix(".html" ); templateResolver.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8" ); templateResolver.setTemplateMode(TemplateMode.HTML); return templateResolver; } @Bean public SpringTemplateEngine templateEngine (ITemplateResolver templateResolver) { SpringTemplateEngine templateEngine = new SpringTemplateEngine (); templateEngine.setTemplateResolver(templateResolver); return templateEngine; } @Bean public ViewResolver viewResolver (SpringTemplateEngine templateEngine) { ThymeleafViewResolver viewResolver = new ThymeleafViewResolver (); viewResolver.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8" ); viewResolver.setTemplateEngine(templateEngine); return viewResolver; } }
这就配置完了,但是Spring的配置文件没写
SpringConfig代替Spring的配置文件 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 package com.zzmr.config;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;@Configuration public class SpringConfig {}
没错里面啥都有没有,用到的时候再配置吧
SpringMVC执行流程 看之前的吧
SSM整合 又到了最后关头
ContextLoaderListener 监听器,Spring提供了监听器ContextLoaderListener,实现ServletContextListener接口,可监听ServletContext的状态,在web服务器启动,读取Spring的配置文件,创建Spring的IOC容器,web应用中必须在web.xml中配置
什么意思呢,就是设置一个监听器,若服务器一启动,就去寻找Spring的配置文件,创建Spring的IOC容器,以便于SpringMVC的Controller层能够实现自动装配service,然后要实现这个功能,要在web.xml中配置
准备工作 pom.xml 以后用到的话,就直接来这里复制了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <project xmlns ="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd" > <modelVersion > 4.0.0</modelVersion > <groupId > com.zzmr.ssm</groupId > <artifactId > ssm_aio</artifactId > <version > 1.0-SNAPSHOT</version > <packaging > war</packaging > <properties > <spring.version > 5.3.1</spring.version > </properties > <dependencies > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework</groupId > <artifactId > spring-context</artifactId > <version > ${spring.version}</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework</groupId > <artifactId > spring-beans</artifactId > <version > ${spring.version}</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework</groupId > <artifactId > spring-web</artifactId > <version > ${spring.version}</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework</groupId > <artifactId > spring-webmvc</artifactId > <version > ${spring.version}</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework</groupId > <artifactId > spring-jdbc</artifactId > <version > ${spring.version}</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework</groupId > <artifactId > spring-aspects</artifactId > <version > ${spring.version}</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework</groupId > <artifactId > spring-test</artifactId > <version > ${spring.version}</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.mybatis</groupId > <artifactId > mybatis</artifactId > <version > 3.5.7</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.mybatis</groupId > <artifactId > mybatis-spring</artifactId > <version > 2.0.6</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > com.alibaba</groupId > <artifactId > druid</artifactId > <version > 1.2.5</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > junit</groupId > <artifactId > junit</artifactId > <version > 4.12</version > <scope > test</scope > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > mysql</groupId > <artifactId > mysql-connector-java</artifactId > <version > 8.0.16</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > log4j</groupId > <artifactId > log4j</artifactId > <version > 1.2.17</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > com.github.pagehelper</groupId > <artifactId > pagehelper</artifactId > <version > 5.2.0</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > ch.qos.logback</groupId > <artifactId > logback-classic</artifactId > <version > 1.2.3</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > javax.servlet</groupId > <artifactId > javax.servlet-api</artifactId > <version > 3.1.0</version > <scope > provided</scope > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId > <artifactId > jackson-databind</artifactId > <version > 2.12.1</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > commons-fileupload</groupId > <artifactId > commons-fileupload</artifactId > <version > 1.3.1</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.thymeleaf</groupId > <artifactId > thymeleaf-spring5</artifactId > <version > 3.0.12.RELEASE</version > </dependency > </dependencies > </project >
SQL 数据库文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 CREATE TABLE `t_emp` (`emp_id` int (11 ) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `emp_name` varchar (20 ) DEFAULT NULL , `age` int (11 ) DEFAULT NULL , `gender` char (1 ) DEFAULT NULL , `email` varchar (50 ) DEFAULT NULL , PRIMARY KEY (`emp_id`)) ENGINE= InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET= utf8
web.xml(WebInit.java) 老师使用xml配置的,我倒是想用注解试一下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 package com.zzmr.config;import org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener;import org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter;import org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilter;import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer;import javax.servlet.Filter;import javax.servlet.ServletContext;public class WebInit extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer { @Override protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() { return new Class []{SpringConfig.class}; } @Override protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() { return new Class []{WebConfig.class}; } @Override protected String[] getServletMappings() { return new String []{"/" }; } @Override protected Filter[] getServletFilters() { CharacterEncodingFilter characterEncodingFilter = new CharacterEncodingFilter (); characterEncodingFilter.setEncoding("UTF-8" ); characterEncodingFilter.setForceEncoding(true ); HiddenHttpMethodFilter hiddenHttpMethodFilter = new HiddenHttpMethodFilter (); return new Filter []{characterEncodingFilter, hiddenHttpMethodFilter}; } @Override protected void registerContextLoaderListener (ServletContext servletContext) { servletContext.addListener(ContextLoaderListener.class); } }
SpringMVC的配置类-WebConfig 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 package com.zzmr.config;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader;import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;import org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver;import org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver;import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.DefaultServletHandlerConfigurer;import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc;import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ViewControllerRegistry;import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;import org.thymeleaf.spring5.SpringTemplateEngine;import org.thymeleaf.spring5.view.ThymeleafViewResolver;import org.thymeleaf.templatemode.TemplateMode;import org.thymeleaf.templateresolver.ITemplateResolver;import org.thymeleaf.templateresolver.ServletContextTemplateResolver;@Configuration @ComponentScan("com.zzmr.controller") @EnableWebMvc public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer { @Bean public ITemplateResolver templateResolver () { WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext = ContextLoader.getCurrentWebApplicationContext(); ServletContextTemplateResolver templateResolver = new ServletContextTemplateResolver (webApplicationContext.getServletContext()); templateResolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/templates/" ); templateResolver.setSuffix(".html" ); templateResolver.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8" ); templateResolver.setTemplateMode(TemplateMode.HTML); return templateResolver; } @Bean public SpringTemplateEngine templateEngine (ITemplateResolver templateResolver) { SpringTemplateEngine templateEngine = new SpringTemplateEngine (); templateEngine.setTemplateResolver(templateResolver); return templateEngine; } @Bean public ViewResolver viewResolver (SpringTemplateEngine templateEngine) { ThymeleafViewResolver viewResolver = new ThymeleafViewResolver (); viewResolver.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8" ); viewResolver.setTemplateEngine(templateEngine); return viewResolver; } @Override public void configureDefaultServletHandling (DefaultServletHandlerConfigurer configurer) { configurer.enable(); } @Override public void addViewControllers (ViewControllerRegistry registry) { registry.addViewController("/" ).setViewName("index" ); } @Bean public CommonsMultipartResolver multipartResolver () { return new CommonsMultipartResolver (); } }
Spring的配置类-SpringConfig 首先一个很重要的知识点,就是@ComponentScan注解的使用,因为我们要对某些类进行排除,Spring对除控制层之外的所有进行扫描,所以应该排除控制层
1 2 3 @ComponentScan( value = "com.zzmr", excludeFilters = {@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,value = Controller.class)})
以上就是排除的用法,FilterType.ANNOTATION就是用注解来排除,后面的value就是注解的class
哈哈哈哈出现问题了吧,配置好扫描组件之后,剩下的就不会配置了,什么数据源啊,整合MyBatis啊,都不会配置
所以啊,我还是去看之前的xml了
断档重开 pom.xml 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <project xmlns ="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd" > <modelVersion > 4.0.0</modelVersion > <groupId > com.zzmr.ssm</groupId > <artifactId > ssm_last</artifactId > <version > 1.0-SNAPSHOT</version > <packaging > war</packaging > <properties > <spring.version > 5.3.1</spring.version > </properties > <dependencies > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework</groupId > <artifactId > spring-context</artifactId > <version > ${spring.version}</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework</groupId > <artifactId > spring-beans</artifactId > <version > ${spring.version}</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework</groupId > <artifactId > spring-web</artifactId > <version > ${spring.version}</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework</groupId > <artifactId > spring-webmvc</artifactId > <version > ${spring.version}</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework</groupId > <artifactId > spring-jdbc</artifactId > <version > ${spring.version}</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework</groupId > <artifactId > spring-aspects</artifactId > <version > ${spring.version}</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework</groupId > <artifactId > spring-test</artifactId > <version > ${spring.version}</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.mybatis</groupId > <artifactId > mybatis</artifactId > <version > 3.5.7</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.mybatis</groupId > <artifactId > mybatis-spring</artifactId > <version > 2.0.6</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > com.alibaba</groupId > <artifactId > druid</artifactId > <version > 1.2.5</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > junit</groupId > <artifactId > junit</artifactId > <version > 4.12</version > <scope > test</scope > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > mysql</groupId > <artifactId > mysql-connector-java</artifactId > <version > 8.0.16</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > log4j</groupId > <artifactId > log4j</artifactId > <version > 1.2.17</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > com.github.pagehelper</groupId > <artifactId > pagehelper</artifactId > <version > 5.2.0</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > ch.qos.logback</groupId > <artifactId > logback-classic</artifactId > <version > 1.2.3</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > javax.servlet</groupId > <artifactId > javax.servlet-api</artifactId > <version > 3.1.0</version > <scope > provided</scope > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId > <artifactId > jackson-databind</artifactId > <version > 2.12.1</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > commons-fileupload</groupId > <artifactId > commons-fileupload</artifactId > <version > 1.3.1</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.thymeleaf</groupId > <artifactId > thymeleaf-spring5</artifactId > <version > 3.0.12.RELEASE</version > </dependency > </dependencies > </project >
web.xml 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <web-app xmlns ="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd" version ="4.0" > <filter > <filter-name > CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name > <filter-class > org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class > <init-param > <param-name > encoding</param-name > <param-value > UTF-8</param-value > </init-param > <init-param > <param-name > forceEncoding</param-name > <param-value > true</param-value > </init-param > </filter > <filter-mapping > <filter-name > CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name > <url-pattern > /*</url-pattern > </filter-mapping > <filter > <filter-name > HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name > <filter-class > org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-class > </filter > <filter-mapping > <filter-name > HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name > <url-pattern > /*</url-pattern > </filter-mapping > <servlet > <servlet-name > SpringMVC</servlet-name > <servlet-class > org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class > <init-param > <param-name > contextConfigLocation</param-name > <param-value > classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value > </init-param > <load-on-startup > 1</load-on-startup > </servlet > <servlet-mapping > <servlet-name > SpringMVC</servlet-name > <url-pattern > /</url-pattern > </servlet-mapping > <listener > <listener-class > org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class > </listener > <context-param > <param-name > contextConfigLocation</param-name > <param-value > classpath:spring.xml</param-value > </context-param > </web-app >
SpringMVC的配置文件 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:mvc ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc https://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd" > <context:component-scan base-package ="com.zzmr.ssm_last.controller" /> <bean id ="viewResolver" class ="org.thymeleaf.spring5.view.ThymeleafViewResolver" > <property name ="order" value ="1" /> <property name ="characterEncoding" value ="UTF-8" /> <property name ="templateEngine" > <bean class ="org.thymeleaf.spring5.SpringTemplateEngine" > <property name ="templateResolver" > <bean class ="org.thymeleaf.spring5.templateresolver.SpringResourceTemplateResolver" > <property name ="prefix" value ="/WEB-INF/templates/" /> <property name ="suffix" value =".html" /> <property name ="templateMode" value ="HTML5" /> <property name ="characterEncoding" value ="UTF-8" /> </bean > </property > </bean > </property > </bean > <mvc:default-servlet-handler /> <mvc:annotation-driven /> <mvc:view-controller path ="/" view-name ="index" > </mvc:view-controller > <bean id ="multipartResolver" class ="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver" /> </beans >
配置Spring的配置文件 整合了MyBatis
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd" > <context:component-scan base-package ="com.zzmr.ssm_last" > <context:exclude-filter type ="annotation" expression ="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller" /> </context:component-scan > <context:property-placeholder location ="classpath:jdbc.properties" > </context:property-placeholder > <bean id ="dateSource" class ="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" > <property name ="driverClassName" value ="${jdbc.driver}" > </property > <property name ="url" value ="${jdbc.url}" > </property > <property name ="username" value ="${jdbc.username}" > </property > <property name ="password" value ="${jdbc.password}" > </property > </bean > <bean id ="transactionManager" class ="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" > <property name ="dataSource" ref ="dateSource" > </property > </bean > <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager ="transactionManager" /> <bean class ="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean" > <property name ="configLocation" value ="classpath:mybatis-config.xml" > </property > <property name ="dataSource" ref ="dateSource" > </property > <property name ="typeAliasesPackage" value ="com.zzmr.ssm_last.pojo" > </property > </bean > <bean class ="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer" > <property name ="basePackage" value ="com.zzmr.ssm_last.mapper" > </property > </bean > </beans >
MyBatis的配置文件 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd" > <configuration > <settings > <setting name ="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value ="true" /> </settings > <plugins > <plugin interceptor ="com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor" > </plugin > </plugins > </configuration >
已经被掏空了,就剩下两个,其实这两个也可以由Spring来配置
其他代码 那也没必要写了,自己明白就行了
好了,我把这个项目的其余功能实现了:添加,删除,修改,测试也没有问题,但是这个项目太简单了啊点这跳转
不过这也算是我的SSM的基础已经学完了,但是我还没有做项目的能力,前端太薄弱了,啥都不会,所以现在学什么?
往后的日子还要加油啊太阳照常升起,日子还要继续